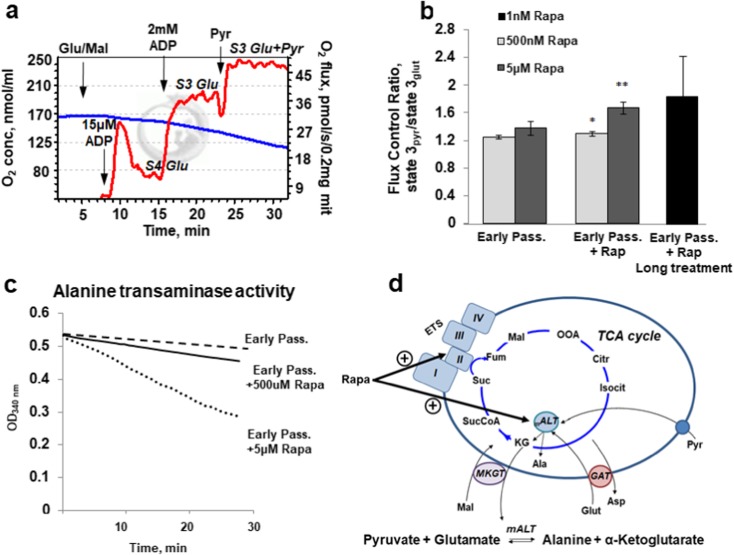
Fig. 4.
Combinatory oxidation of glutamate, malate, and pyruvate by isolated cardiac mitochondria. a The original oxygraphic protocol applied to study of oxidation of the substrate combination. Addition of 15 μM of ADP enabled to evaluate state 4 and addition of 2 mM ADP to read out the maximal state 3 respiration rates. Sequential addition of 10 mM glutamate and 2 mM malate and then 10 mM pyruvate gave higher rates of oxygen consumption than the glutamate and pyruvate alone. b Quantitative flux control ratios were obtained as state 3pyr/state 3glut. Pre-incubation of mitochondria with rapamycin for 1 h dose-dependently elevated glutamate/malate/pyruvate oxidation. Elevation of pyruvate oxidation over glutamate/malate was also observed in mitochondria isolated from cells long treated with rapamycin for 14 days. Data are mean ± SD; *p < 0.044, **p < 0.0021. c Alanine aminotransferase activity also dose-dependently elevates in the presence of rapamycin. d The schematics demonstrates transamination of pyruvate and glutamate by mitochondria matrix alanine aminotransferase and the formed α-ketoglutarate further converts in TCA cycle to succinate and activates succinate dehydrogenase-dependent respiration. Abbreviations: ETS, electron transport system; mALT, mitochondria alanine aminotransferase; MKGT, malate-α-ketoglutarate transporter; GAT, glutamate-aspartate transporter