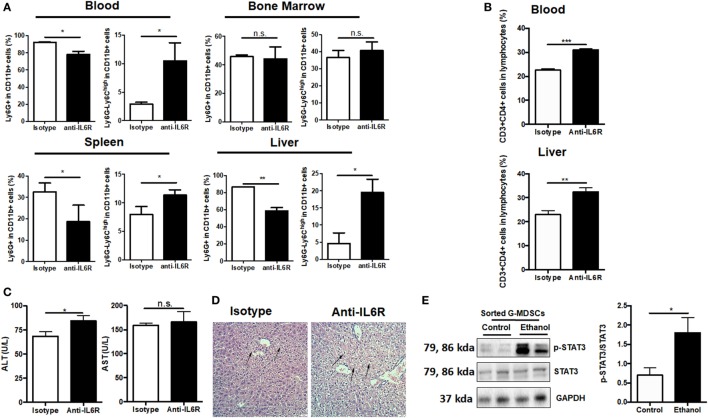
Figure 6.
Role of IL-6 in mediating the expansion of granulocytic-MDSCs (G-MDSCs) populations. Anti-IL6R antibody (Bio X cell) or isotype antibody was injected i.p. into mice at a dose of 150 mg/kg per mouse (n = 6 for each group). The populations of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and T cells in blood and liver were determined by flow cytometer and then liver function was evaluated via serological and histological examination. (A) Population of MDSCs from the blood, spleen, liver, and bone marrow of mice treated with anti-IL6R or isotype antibody. (B) Population of cytotoxic T cells and T helper cells in blood and liver of mice treated with anti-IL6R or isotype antibody. (C) Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level in serum of mice treated with anti-IL6R or isotype antibody. (D) H&E staining images of liver tissues from mice treated with anti-IL6R or isotype antibody. The hepatocellular apoptosis and single cell necrosis were indicated by arrows. (E) Expression of p-signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3), and STAT3 in G-MDSCs sorted from mice treated with ethanol or vehicle detected by western blotting. Data were analyzed as mean value ± SD and Student’s T-test was used to assess the result significance. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared with the control group; n.s., not significant.