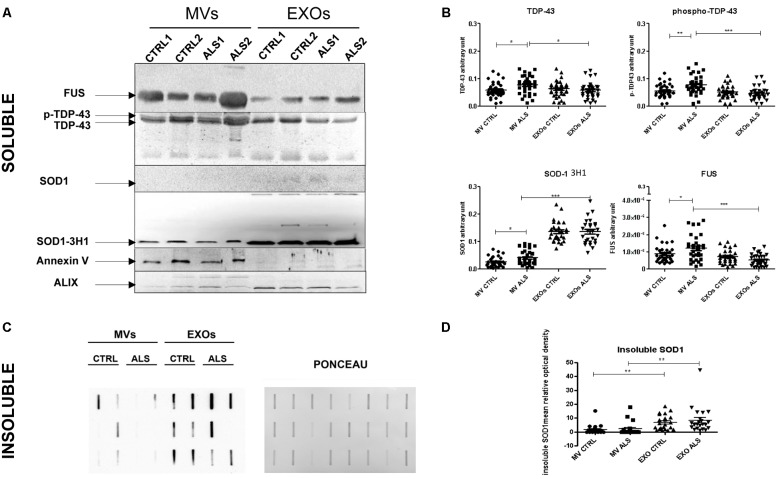
FIGURE 4.
Plasma derived MVs from ALS patients are enriched with pathological proteins compared to controls. (A) SOD1, TDP-43, and FUS detection by Western Blot analysis in the soluble fraction of MVs and EXOs derived from plasma of 2 ALS and 2 healthy donors. Annexin V and Alix were used as marker control for MVs and EXOs. SOD1, recognized by specific antibody 3H1 (but not by polyclonal antibody anti-SOD1) was present in MVs and EXOs of ALS patients compared to healthy controls. TDP-43 bands and FUS were recognized in MVs and in EXOs. Images are cropped for clarity and full figures are shown in Supplementary Figures 2–4; (B) TDP-43, p-TDP-43, SOD1, and FUS densitometric analysis in MVs and EXOs soluble fraction from 30 ALS patients and matched controls. (ANOVA test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001). ALS patients have an increased level of SOD1, TDP-43, FUS level in MVs compared to controls. No variation was observed in EXOs of patients and controls; (C) SOD1 insoluble fraction in MVs and EXOs from 6 CTRLs and 6 ALS patients. Example of filter retardation assay probed with polyclonal anti-SOD1 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, United States) and its Ponceau; (D) SOD1 densitometric analysis in MVs and EXOs insoluble fraction from 22 ALS patients and matched controls. (ANOVA test, ∗∗P < 0.01). SOD1 protein level was not different between ALS and CTRLs group neither in MVs and EXOs but the real difference was between EXOs and MVs, since the latter have less protein than the first.