Figure 2.
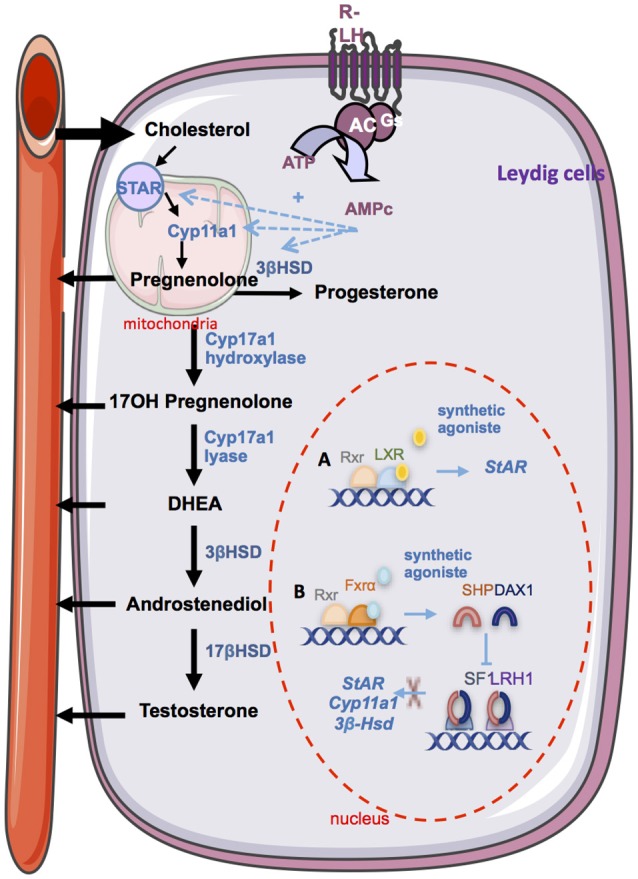
The endocrine function. Steroidogesesis occurs in Leydig cells from cholesterol. The first step involves the STAR protein which allow the transport of cholesterol within the mitochondria. Then, cholesterol is converted in pregnenolone by the CYP11A1 enzyme. Several enzymatic transformation steps will convert pregnenolone into testosterone. The differents enzymes are marked in blue. LH via it receptor (R-LH) induces the increase expression of some key enzymes of spermatogenesis. Some nuclear receptors have been described as regulators of spermatogenesis. (A) The activation of LXRs by a synthetic agonist induces the upregulation of Star. (B) The activation of FXRα by a synthetic agonist induce the increase Shp of Dax1 which in turn inhibits the trans activating activity of SF1 and LRH1 on the promotor of steroidogenic enzyme such as Star, Cyp11a1, and 3bhsd. STAR, steroidogenic acute regulatory protein; Cyp11a1, cytochrome p450scc cholesterol side chain clivage; Cyp17a1, cytochrome P450 17α-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase; 3βHsd, 3β·hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; 17βHsd, 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; DHEA, dehydroepiandrosterone; RXR, retinoid acid receptor; LXR, liver X receptor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; Shp, small heterodimer partner; Dax1, dosage-sensitive sex reversal, adrenal hypoplasia critical region, on chromosome X, gene 1; SF1, steroidogenic factor 1; LRH1, liver receptor homolog 1.
