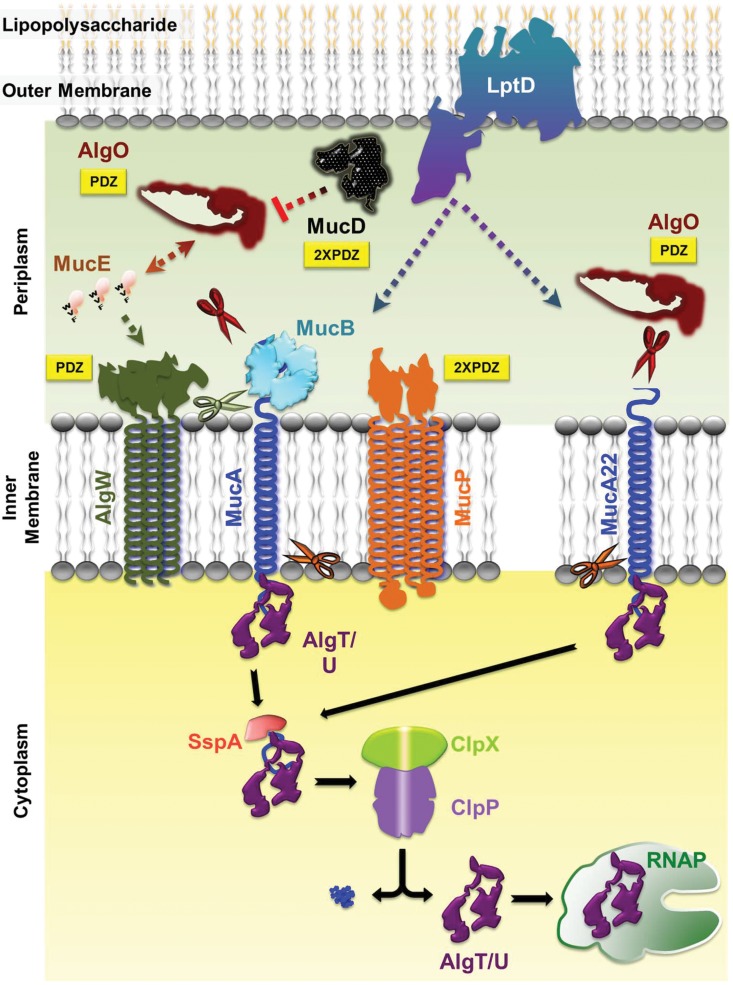
FIG 1.
Regulated intramembrane proteolysis pathway of P. aeruginosa. The C-terminal WVF motif of MucE indirectly activates the AlgW protease to cleave MucA. This cleavage requires the removal of the MucB protein from the MucA C terminus. Subsequent cleavage of MucA is performed by the AlgO and MucP proteases, which releases the AlgT/U sigma factor. Further processing by SspA, ClpX, and ClpP removes the remaining MucA fragment, allowing AlgT/U to interact with RNA polymerase (RNAP) and begin transcription of the alginate pathway genes. This process is negatively regulated in the periplasmic space by MucD. In the mucoid mucA22 mutant, the truncated C terminus of the protein is not bound by MucB, allowing for cleavage by the AlgO protease (see the text for details). The cleaved MucA22 protein is then processed by SspA, ClpX, and ClpP. Both wild-type and MucA22 pathways also undergo regulation by the LptD outer membrane protein (46). AlgO, MucD, AlgW, and MucP all contain PDZ domains (yellow boxes) involved in protein-protein interactions. Scissors indicate proteolytic cleavage of MucA or MucA22 by AlgW (green), AlgO (burgundy), and MucP (orange).