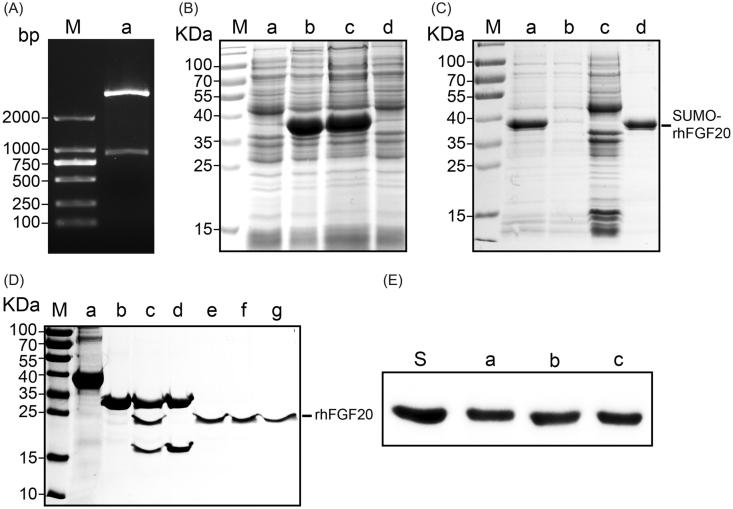
Figure 1.
Soluble expression and purification of rhFGF20. (A) Agarose gel electrophoresis showing the molecular weight of the insert DNA comprising the SUMO-rhFGF20 DNA sequence (lane a, lower band ∼1000 bp) and the backbone of pET20 expression vector (lane a, upper band >2000 bp). (B) SDS–PAGE gel showing expression of SUMO-rhFGF20. Lane M: protein molecular weight markers; lane a: bacterial lysate before IPTG induction; lane b: bacterial lysate after induction by 1 mM IPTG; lane c: soluble supernatant fraction after centrifugation; lane d: insoluble fraction of the bacterial lysate after low-speed centrifugation. (C) SDS–PAGE gel analysis for fractions from Ni–NTA agarose column. Lane M: protein molecular weight markers; lane a: loading sample; lane b: flow through; lane c: wash fraction; lane d: fraction eluted from Ni column. (D) Source Q purification following digestion by SUMO protease. Lane M: protein molecular weight markers; lane a: IMAC purified SUMO-rhFGF20; lane b: SUMO protease; lane c: sample after enzyme digestion; lane d: SUMO protease and SUMO eluted from Source Q column; lane e–g: purified rhFGF20. (E) Immunoblotting of the purified rhFGF20 detected using anti-human FGF20 antibody. Lane S: standard rhFGF20 sample; Lane e–g: purified rhFGF20.