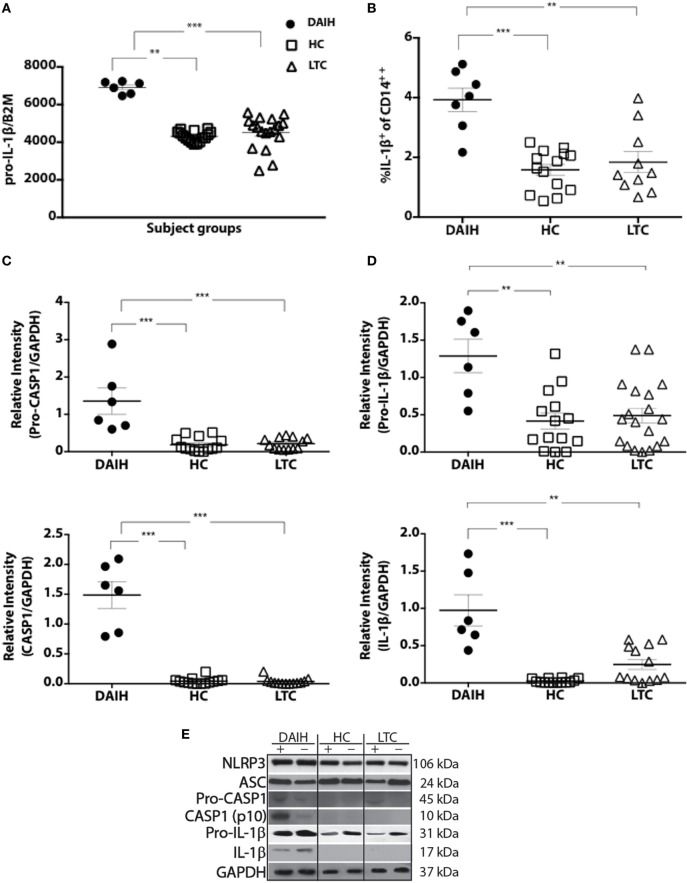
Figure 1.
CD14++ monocytes from liver transplanted patients with de novo autoimmune hepatitis (DAIH) undergo inflammasome activation. CD14++ monocytes from liver transplanted patients with DAIH (n = 7) and without DAIH (LTC) (n = 18) and healthy, non-transplanted children (HC) (n = 16) were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 24 h and (i) subjected to qPCR for pro-IL-1β; (ii) stained with anti-CD3, anti-CD14, intracellular IL-1β. Cytokine secretion analyzed using flow cytometry; (iii) subjected to Western Blot for NLRP3, ASC, pro-caspase-1, caspase-1, IL-1β. (A) CD14++ monocytes from patients with DAIH expressed significantly more pro-IL-1β compared to CD14++ monocytes from liver transplanted patients with normal allograft function and no DAIH (LTC) (p < 0.001), as well as CD14++ monocytes from healthy, non-transplanted children (HC) (p = 0.002). (B) CD14++ monocytes from patients with DAIH produced significantly more IL-1β compared to CD14++ monocytes from liver transplanted patients with normal allograft function and no DAIH (LTC) (p = 0.005), as well as CD14++ monocytes from healthy, non-transplanted children (HC) (p < 0.001). (C–E) Significant pro-caspase and caspase-1 cleavage observed in CD14++ monocytes from patients with DAIH compared to CD14++ monocytes from LTC (p < 0.001; p < 0.001) and HC (p < 0.001; p < 0.001). Significant pro-IL-1β and IL-1β production observed in CD14++ monocytes from patients with DAIH compared to CD14++ monocytes from LTC (p = 0.007; p = 0.002) and HC (p = 0.006; p < 0.001). Representative blot for three patients from each subject group. Plus sign indicates with LPS stimulation, minus sign indicates absence of LPS stimulation.