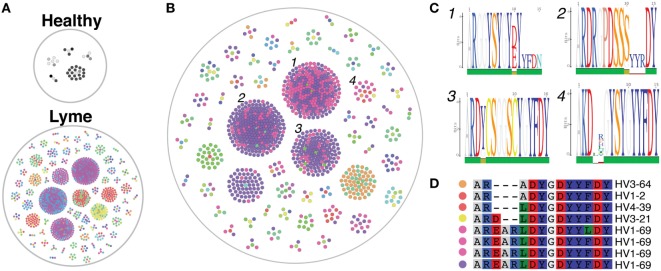
Figure 6.
Heavy-chain immunoglobulin sequencing of bulk mRNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBCs) derived from untreated Bb-infected patients reveals disease-specific CDR3 sequence motifs. Bulk heavy-chain CDR3 sequences from PMBCs of untreated Lyme disease patients and healthy controls were clustered using the cd-hit algorithm to identify convergent sequence motifs. A total of 379,457 full-length error-corrected VDJ sequences were included in the analysis. Each dot represents a sequenced antibody clone, with colors representing individual subjects. (A) Clusters were filtered based on those containing at least three separate subjects, and the size and number of these convergent clusters visualized using the igraph package in R. Healthy controls revealed only five cross-patient clusters, while numerous convergent clusters were revealed untreated Lyme disease patients. (B,C) Convergent clusters present in at least three separate Lyme subjects (B), but not present in any healthy controls were visualized using igraph, and individual sequences from four clusters with multiple subjects were aligned to display specific sequence motifs (C). (D) Sequence alignment of cluster 4, which includes five separate Bb-infected patients, including the predicted V gene used by each clone. Colored dots correspond to matching subjects in panel (B).