Fig. 6.
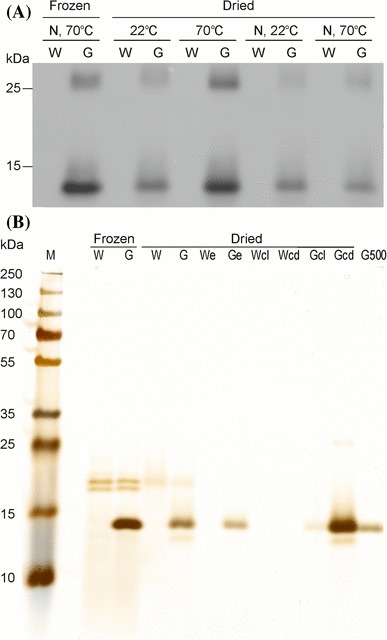
Extraction of griffithsin from dried tobacco leaves. a Western blot analysis of griffithsin accumulation in dried leaves. TSP was extracted from frozen or dried leaves of griffithsin-producing transplastomic (G) and wild-type plants (W). Leaves that had been dried and stored for 4 months were compared to leaves that had been frozen and stored at − 80 °C until use. 200 µL buffer were added per 100 mg ground frozen leaf material. To compensate for water loss, 29 µL/mg buffer were added to ground dried leaf material. All extractions were performed with ‘pH 4’ buffer with an incubation step at either 22 or 70 °C for 15 min. The effect of freezing the dried tobacco samples in liquid nitrogen before grinding (N) was also tested. Griffithsin and its dimer were immunodetected with a griffithsin-specific antibody. b Silver-stained SDS-PAA gel (10%) illustrating the purification of griffithsin from dried leaves. Extraction was performed as in a. The eluate (e) was ultrafiltrated resulting in a color gradient of an upper light-colored fraction (cl) and a more dark-colored lower fraction (cd). 500 ng of 6xHis-tagged griffithsin purified from E. coli was loaded as a reference (G500). The loaded eluate volumes were adjusted to allow for quantitative comparison of input and eluate
