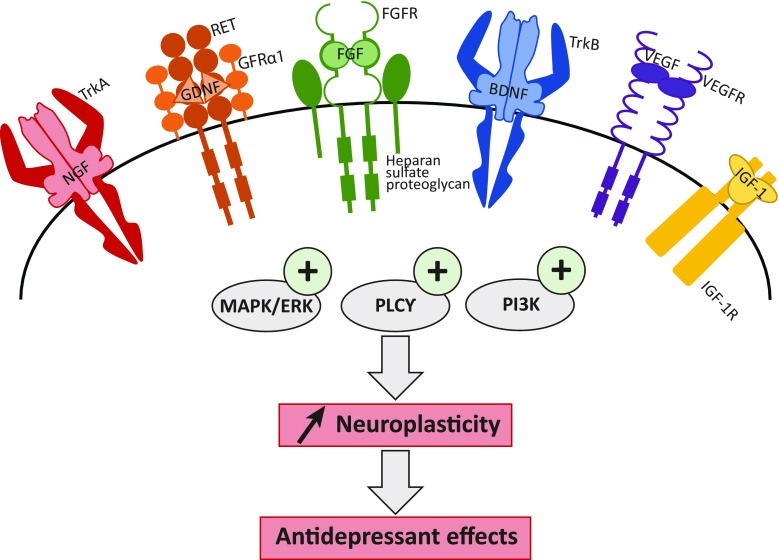
Fig. 3.
Neurotrophins increase neuroplasticity through the activation of three main signaling pathways. Neurotrophins bind to their receptors in order to promote three main signaling pathways: the MAPK/ERK, the PI3-K, and the PLCγ signaling cascades. Once activated, they stimulate neuroplasticity, especially synaptic plasticity, neurotransmission and neuronal survival, growth, and differentiation. An increase of neuroplasticity is likely to induce antidepressant effects. BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; TrkB, tropomyosin-related kinase receptor B; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; GDNF, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; GFRα1, GDNF-family receptor-α; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IGF-1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; NGF, nerve growth factor; TrkA, tropomyosin-related kinase receptor A