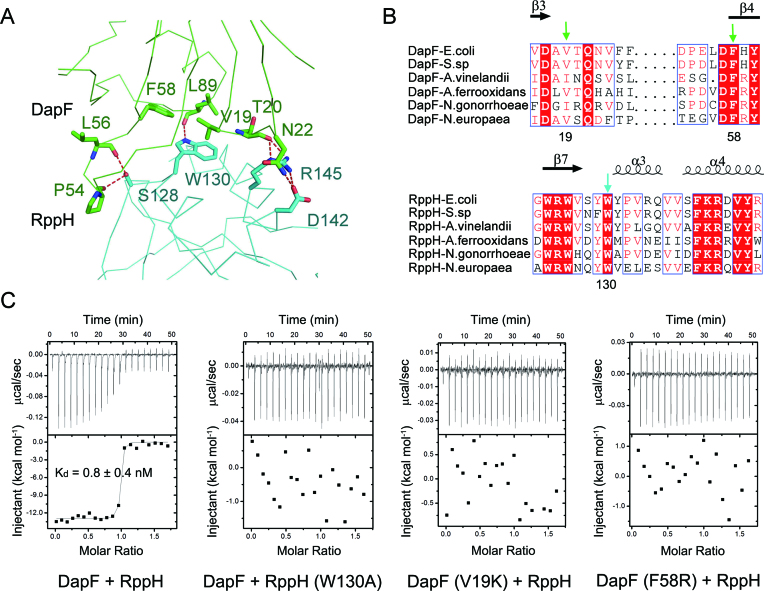
Figure 4.
The interface between DapF and RppH. (A) Close-up view of the interface of DapF and RppH. Residues forming the interface of DapF and RppH are shown as green and cyan sticks, respectively. Red dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds. (B) Partial sequence alignment results of DapF homologues and RppH homologues. Secondary structural elements are indicated above. Completely conserved amino acids are colored in red, and partially conserved amino acids are enclosed in blue boxes. V19 and F58 on DapF, and W130 on RppH are key residues supporting the interface of DapF–RppH compl ex and are indicated by green and cyan arrows, respectively. (C) Interaction of DapF and RppH detected by isothermal titration calorimetry. Wild-type DapF binds RppH with a dissociation constant of ∼0.8 nM. Mutation of either RppH (W130A) or DapF (V19K or F58R) abolishes their interaction.