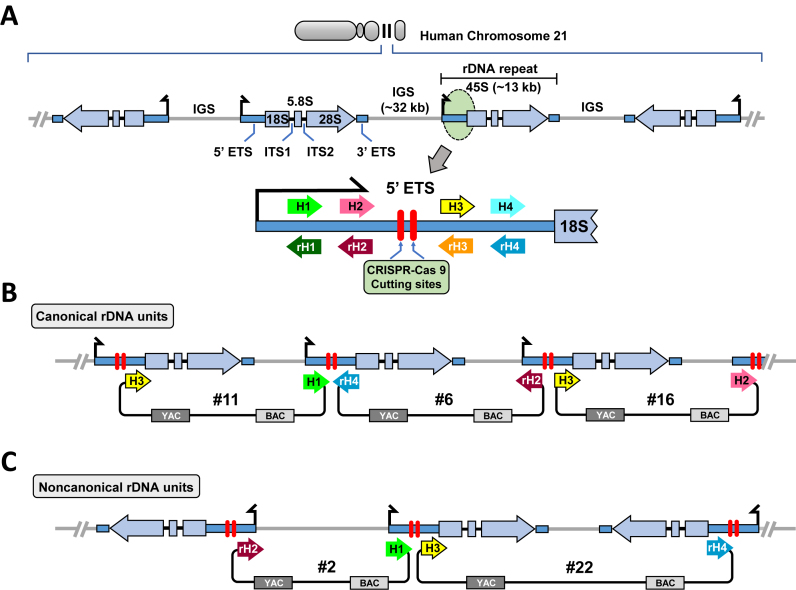
Figure 1.
Scheme for isolation of human ribosomal DNA from mouse/human hybrid cell line as circular YAC/BAC. (A) Schematic representation of rDNA cluster in human acrocentric chromosomes 21. Both canonical rDNA units organized as a tandem repeats and rDNA units forming palindromic structure are shown. Each unit is composed of an ∼13 kb transcribed region encoding 45S rRNA (5′ ETS, 18S, ITS1, 5.8S, ITS2, 28S and 3′ ETS) and an ∼32 kb IGS. All four targeting sequences for TAR vectors, hooks (H1, H2, H3 and H4), were chosen from the 5′ ETS region that is ∼1.4 kb upstream of the 18S rRNA. Human rDNA could be cleaved at the two positions between H2 and H3 by the Cas9–gRNA complexes (red bars). (B) Scheme for TAR cloning of rDNA organized as tandem repeats. Three TAR vectors, #11, #6 and #16, with canonical orientation of the hooks are shown. Homologous recombination between the targeting sequences in the vectors and a targeted human rDNA fragment leads to the establishment of a circular YAC/BAC. (C) Scheme illustrating TAR cloning of rDNA sequences organized as a palindrome. Two TAR vectors, #2 and #22, in which one hook is inverted (rH2 or rH4) were constructed. Homologous recombination between the targeting sequences in the vectors and the targeted human rDNA fragment may lead to the establishment of a circular YAC/BAC only for regions with a palindromic structure. (ETS: External transcribed spacer; ITS: Internal transcribed spacer).