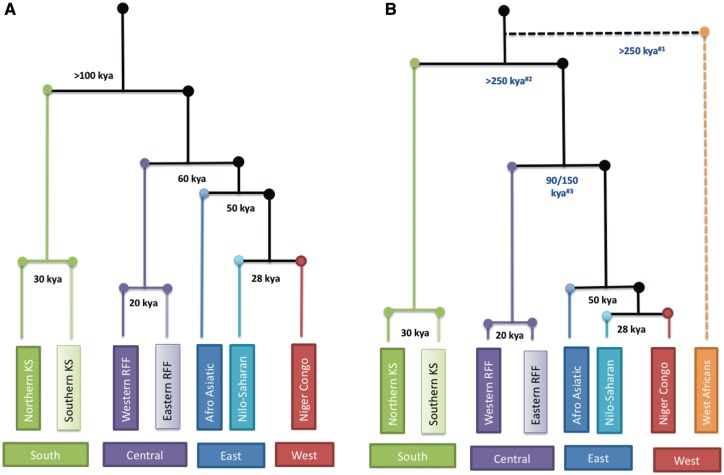
Figure 1.
Major early African population splits showing our understanding prior to and after the availability of WGS data and novel analysis approaches. The events of the past ∼5000 years, prior to the Bantu expansion are not shown and therefore the African regions (South, Central, East and West) reflect the groups that predominated in these regions at ∼5000 years ago (kya). Both trees are rooted to the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) and the estimated major splits are shown in kya. (A) shows our understanding prior to ∼2016 when the MRCA was estimated to be ∼150 kya and (B) following further analyses that place the MRCA at ∼300 kya, with revised estimates of major splits shown in blue. The length of the branches are not to scale. The dotted line shows the recently proposed deep split of a western African ancestry population ∼250 kya. #1Skoglund et al. (12); #2Schlebusch et al. (9); #3Hsieh et al. (10). KS: Khoesan; RFF: Rain Forest Foragers.