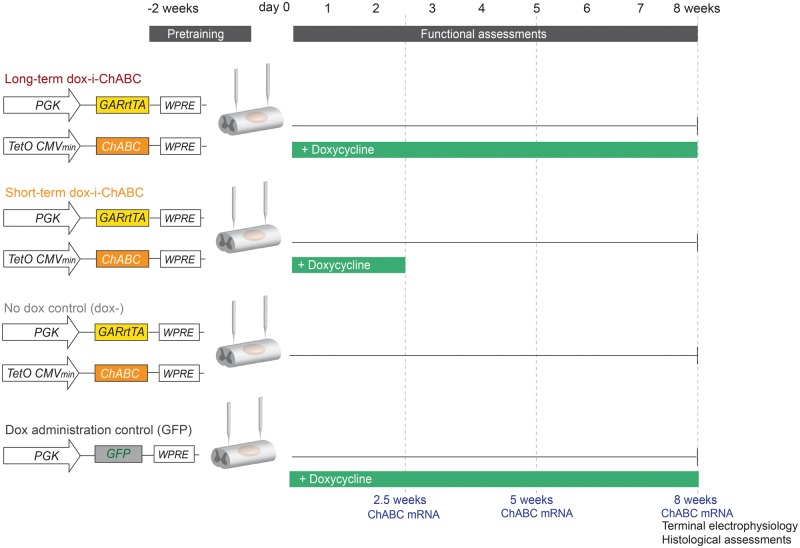
Figure 3.
Dox-i-ChABC study design. To validate the on/off switch over time and assess functional efficacy of long term versus short term dox-i-ChABC, animals were randomly assigned to four treatment groups following pretraining in behavioural tasks and midline cervical 225 kdyn contusion injury (dox administration is in green): (from top to bottom) Dox-i-ChABC vectors with doxycycline administration sustained for the 8 week duration of the study (long-term dox-i-ChABC); Dox-i-ChABC vectors with doxycycline administration for the first 2.5 weeks (short-term dox-i-ChABC); Dox-i-ChABC vectors without doxycycline administration (dox−); and GFP vector injection with doxycycline administration throughout (GFP), to control for broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment. Additional animals were also included to assess ChABC gene expression at different time points throughout the experiment (dotted lines). Terminal electrophysiology and histological assessments were performed after the final behavioural time point.