Fig. 1. trp53 deficiency alters the growth effects of tumor suppression in KrasG12D-driven lung tumors in vivo.
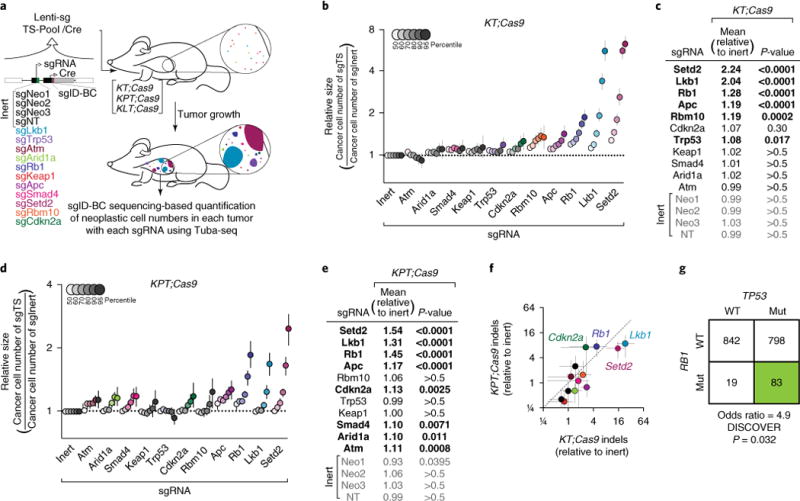
a, Tuba-seq approach to study combinatorial tumor suppressor inactivation in vivo. Tumors were initiated with Lenti-sgTS-Pool/Cre (containing four inert sgRNA vectors and eleven vectors targeting known and candidate tumor suppressor genes) in three different genetically engineered mouse backgrounds: KrasLSL-G12D/+; Rosa26LSL-tdTomato; H11LSL-Cas9 (KT;Cas9), KT; Trp53flox/flox; Cas9 (KPT;Cas9) and KT; Lkb1flox/flox; Cas9 (KLT;Cas9). Each sgRNA vector contains a unique sgID and a random barcode, which was used to quantify individual tumor sizes via deep sequencing. b, Analysis of relative tumor sizes in KT;Cas9 mice 15 weeks after tumor initiation. Relative size of tumors at the indicated percentiles is merged data from 10 mice, normalized to the average size of sgInert tumors. Error bars throughout this study denote 95% confidence intervals determined by bootstrap sampling. Percentiles that are significantly different from sgInert are in color. c, Estimates of mean tumor size, assuming a log-normal tumor size distribution, identified sgRNAs that significantly increased growth in KT;Cas9 mice. Bonferroni-corrected, bootstrapped P-values are shown. sgRNAs with P < 0.05 are bold. d,e, Same as b,c, except for merged data from 12 KPT;Cas9 mice. f, Abundance of indels at targeted loci relative to median of genome-targeting inert sgRNAs Neo1–Neo3. Coloring according to a. g, Functional mutations in TP53 and RB1 in human lung adenocarcinomas from TCGA and GENIE datasets (see URLs; N = 1,792). RB1 and TP53 alterations co-occur, as predicted from Tuba-seq fitness measurements. WT, wild type; Mut, mutated.
