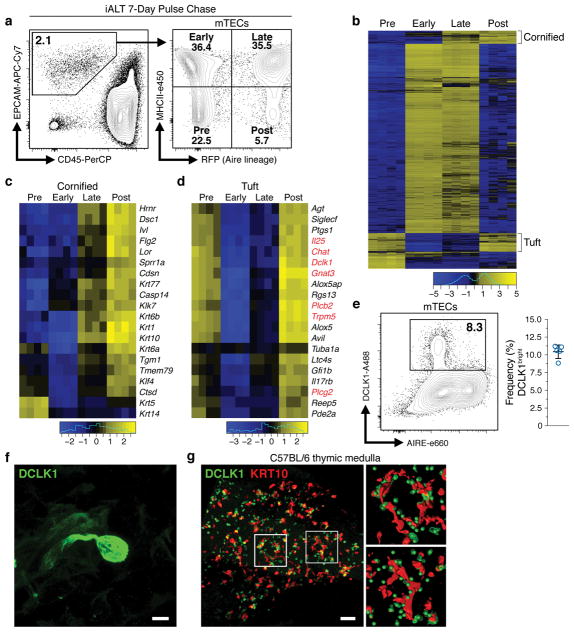
Figure 1. Tuft-like cells are closely associated with cornified bodies in the thymic medulla.
a, Gating of mTEC subsets within CD11c− CD45− EPCAM+ thymic epithelial cells. Sorted in quadruplicate for RNA-seq (12 pooled thymi per replicate, n = 4 sorted replicates). b, Heatmap of differentially expressed genes (FDR < 0.01 and |FC| > 8). c, d, Selected genes from regions marked ‘Cornified’ or ‘Tuft’. Log2 fold change relative to mean expression. e, DCLK1 intracellular staining in mTECs (mean +/− SD). n = 5 mice; 3 independent experiments. f, Confocal maximum projection of a DCLK1bright cell. Scale, 5 μm. n = 5 mice, 3 independent experiments. g, Confocal maximum projection (z = 77 μm) of a medullary region at low magnification. Right, regions of interest (white squares) with KRT10 converted to surfaces and DCLK1 converted to center of intensity coordinates. Scale, 100 μm. n = 3 thymic slices, 2 independent experiments.