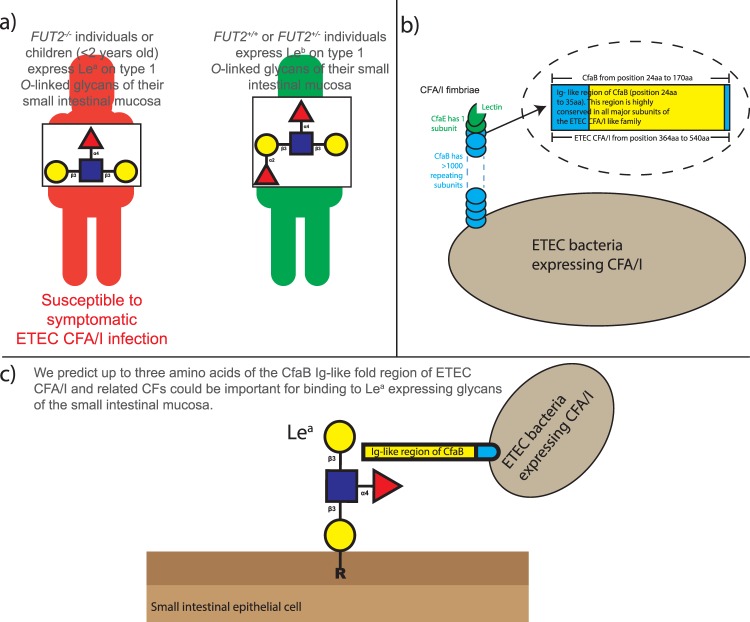
Figure 6.
Working hypothesis. (a) FUT2−/− individuals or children (<2 years old) express Lea on type 1 O-linked glycans of the small intestinal mucosa. We have evidence to suggest they are susceptible to symptomatic ETEC CFA/I (and related CFA/I CF family members) infection. FUT2+/+ or FUT2+/− individuals (>2 years old) express Leb on type 1 O-linked glycans of the small intestinal mucosa. We have not found these individuals to not be susceptible to ETEC CFA/I (and related CFA/I CF family members) infection. (b) ETEC CFA/I fimbriae contains >1,000 copies of a major subunit (CfaB), with one or a few copies of the tip residing minor subunit (CfaE). A 12-aa stretch V24EKNITVTASVD35 of the Ig-like binding groove region of CfaB served as a CFA/I docking site our in-silico docking analysis. This 12 amino acid stretch also shares structural similarities with all ETEC CF major subunits of the CFA/I CF like family, and with class 1 pili from bacteria that can cause urinary and respiratory infections by binding to host glycolipids containing HBGAs. (c) Using our small intestinal like glycan defined CHO-K1 cell lines, we have demonstrated that CfaB of ETEC CFA/I fimbriae, as well as four related CFs, bind more to our CHO-K1 cell-line expressing Lea, compared to cells carrying Leb or the CHO-K1 wild-type glycan phenotype. Using in-silico docking analysis, we predict up to three amino acids (Glu25, Asn27, Thr29) found in the immunoglobulin (Ig)-like groove region of CfaB of CFA/I and related CF fimbriae, could be important for the preferential and higher affinity binding of CFA/I fimbriae to Lea glycans. These findings may lead to a better molecular understanding of ETEC pathogenesis, aiding in the development of vaccines and/or anti-infection therapeutics, which block such host-pathogen interactions.