Fig. 1.
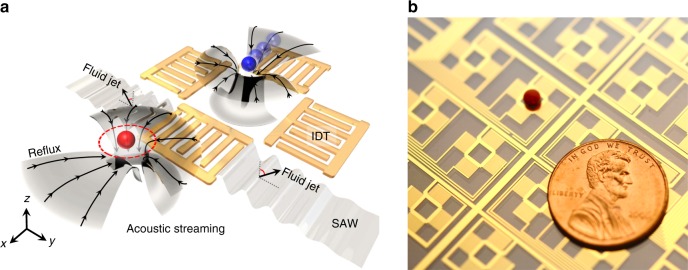
Digital acoustofluidics for contactless and programmable droplet manipulation. a Schematic showing one unit consisting of four IDTs (one pixel) in the digital acoustofluidic device. The four IDTs can be selectively excited to translate droplets along the ±x and ±y directions. The aqueous droplets are isolated from the piezoelectric substrate by an inert carrier fluid to prevent direct contact with surfaces. The IDT (bottom left) embedded beneath the carrier fluid generates SAWs that pumps out fluid in the ±y directions and pumps in fluid in the ±x directions. The red and blue droplets are separately trapped at the two symmetric hydrodynamic wells near the flanks of an IDT. The blue droplet is translated toward a well on the other side of the excited transducer. The reflux streamlines are shown in black. b A photo showing the digital acoustofluidic device with a drop of blood floating on the carrier layer of fluorinated oil