Fig. 9.
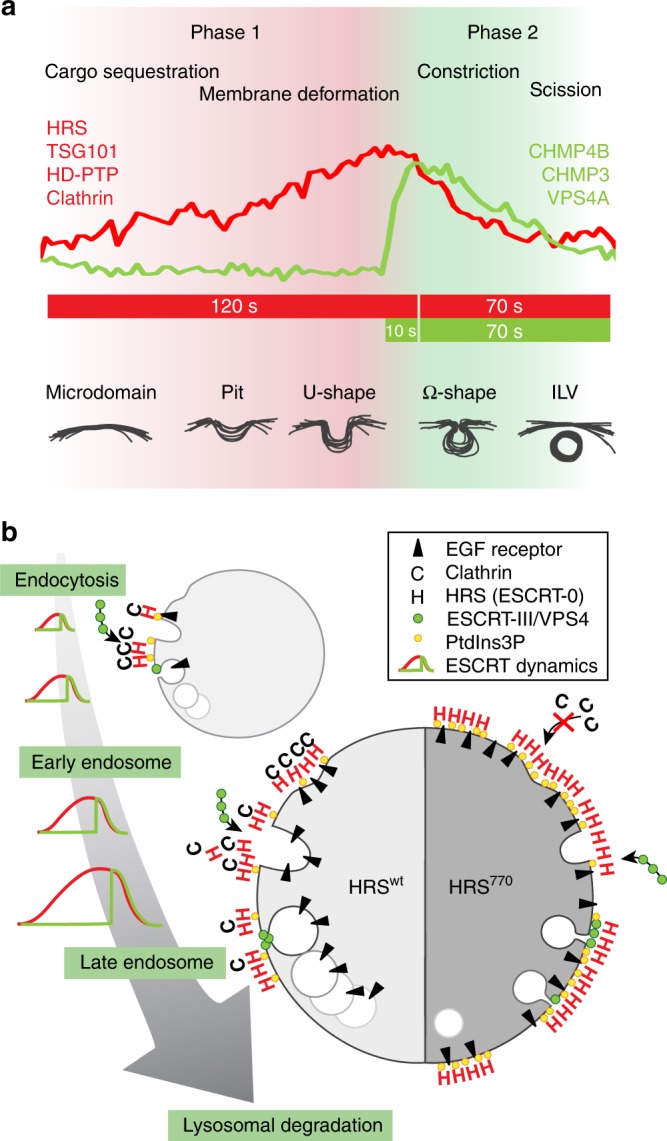
Models of ESCRT-dependent ILV formation. a Model combining ESCRT kinetics with the timing of ILV formation. Phase 1: HRS and clathrin slowly accumulate on the endosome membrane, where they sequester cargo into a sorting microdomain, visible as an electron-dense EGFR-containing HRS/clathrin coat. TSG101 and HD-PTP show similar undulating kinetics. Based on our findings with the clathrin-binding mutant of HRS, we suggest that the first phase comprises both cargo sorting and membrane deformation. Phase 2: ESCRT-III and VPS4A show a rapid accumulation which may reflect polymerization of ESCRT-III subunits and simultaneous recruitment of VPS4A, followed by a concerted dissociation of all ESCRT complexes. We suggest that the second phase may correspond to constriction and scission of ILVs. For details see Discussion. b Model of ESCRT-dependent ILV formation and the role of clathrin. Left: to ensure efficient cargo degradation in lysosomes, ESCRT proteins and clathrin are recruited to endosomes as they mature, in a coordinated and repetitive wave-like pattern. Each wave (which lasts for about 200 s) correlates with the formation of one ILV. Right: in the absence of endosomal clathrin, the wave dynamics are disturbed, ESCRT-0 and cargo accumulate on the endosomal membrane, and ILV formation is perturbed; the size of the forming bud is smaller, the forming ILV has a longer neck, and the diameter of the few ILVs that do form is smaller
