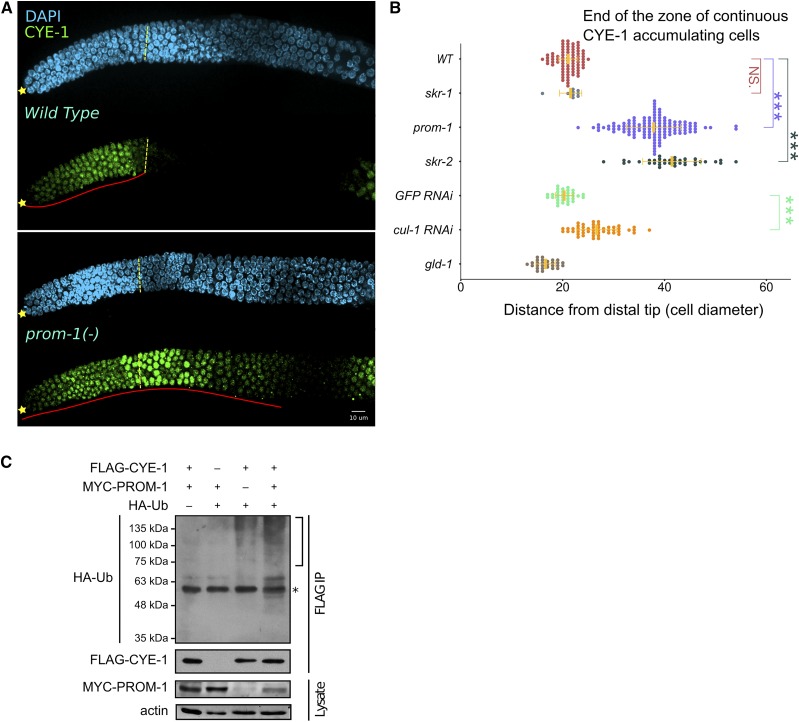
Figure 2.
SCFPROM-1 is required for downregulation of CYE-1 at meiotic entry. (A) Images of CYE-1-stained (green) distal wild-type (top) or prom-1 mutant (bottom) germlines from dissected young adult hermaphrodites, costained with DAPI (cyan). ☆’s indicate distal gonadal end. Dashed yellow lines indicate position of overt meiotic entry; see Materials and Methods for how the position of overt meiotic entry was determined here and in other figures. Solid red lines highlight the zone of continuous CYE-1 accumulation. (B) Graph showing distance, in cell diameters, between the DT of the germline and the row of cells at proximal end of the continuous zone of CYE-1 staining [solid red line in (A)] for young-adult hermaphrodites of indicated genotype. cul-1 RNAi, here and in other figures, was performed in worms of the genotype jamSi2[mex-5p::rde-1(+)] II; rde-1(ne219) V to largely restrict RNAi knockdown to the germline. Data are plotted as horizontal dot plots with each dot representing length in cell diameter to zone end for one gonad. Thick vertical lines represent mean and horizontal lines represent mean ± SD. P-value ≤ 0.01 (*); ≤ 0.001 (**); ≤ 0.0001 (***); > 0.01 non-significant (NS.). (C) Different combinations of C. elegans FLAG-CYE-1, MYC-PROM-1, and HA-ubiquitin (HA-UB) constructs were transiently expressed in HEK293T cells, followed by FLAG-CYE-1 immunoprecipitation (IP). The immunoprecipitants were analyzed by Western blot with anti-HA and anti-FLAG antibodies. Slower migrating polyubiquitinated forms of CYE-1 are slightly increased in the presence of PROM-1 (see text). The expression of MYC-PROM-1 was analyzed in whole cell lysates. The bracket marks polyubiquitination of CYE-1. * represents cross-reactivity between the mouse anti-FLAG antibody used for IP and the rat anti-HA antibody. WT, wild type.