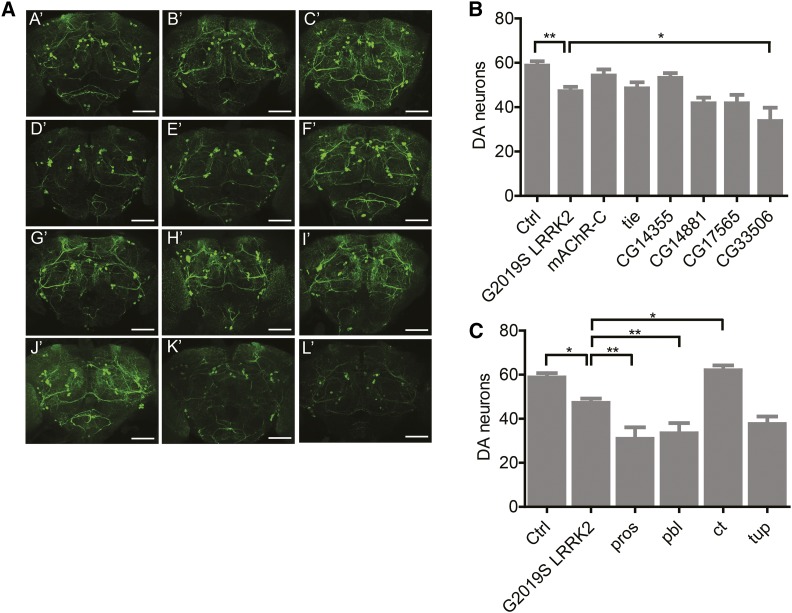
Figure 3.
Effect of candidate modifier gene KD on LRRK2 G2019S dopamine neuron loss. (A) Confocal projection images through the brain of control +/+; UAS-LRRK2-G2019S/+ (A′), and Ddc-GAL4/+; UAS-LRRK2-G2019S/+ (B′) flies and G2019S LRRK2 expressing flies with RNAi-mediated knockdown of mAChR-C (C′), tie (D′), CG14355 (E′), CG14881 (F′), CG17565 (G′), CG33506 (H′), pros (I′), pbl (J′), ct (K′) and tup (L′). Bar, 60 μM. Quantitation of total dopamine neurons in five clusters (PPM1/2, PPM3, PPL1, PPL2, and PAL) for top association (B) and neuron projection (C) candidate genes. There was a significant effect of genotype for both (individual ANOVAs, P < 0.0001) and Bonferroni post-tests revealed a significant effect of G2019S LRRK2 expression and KD of CG33506, pros, pbl and ct candidate modifiers (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01).