Fig. 3.
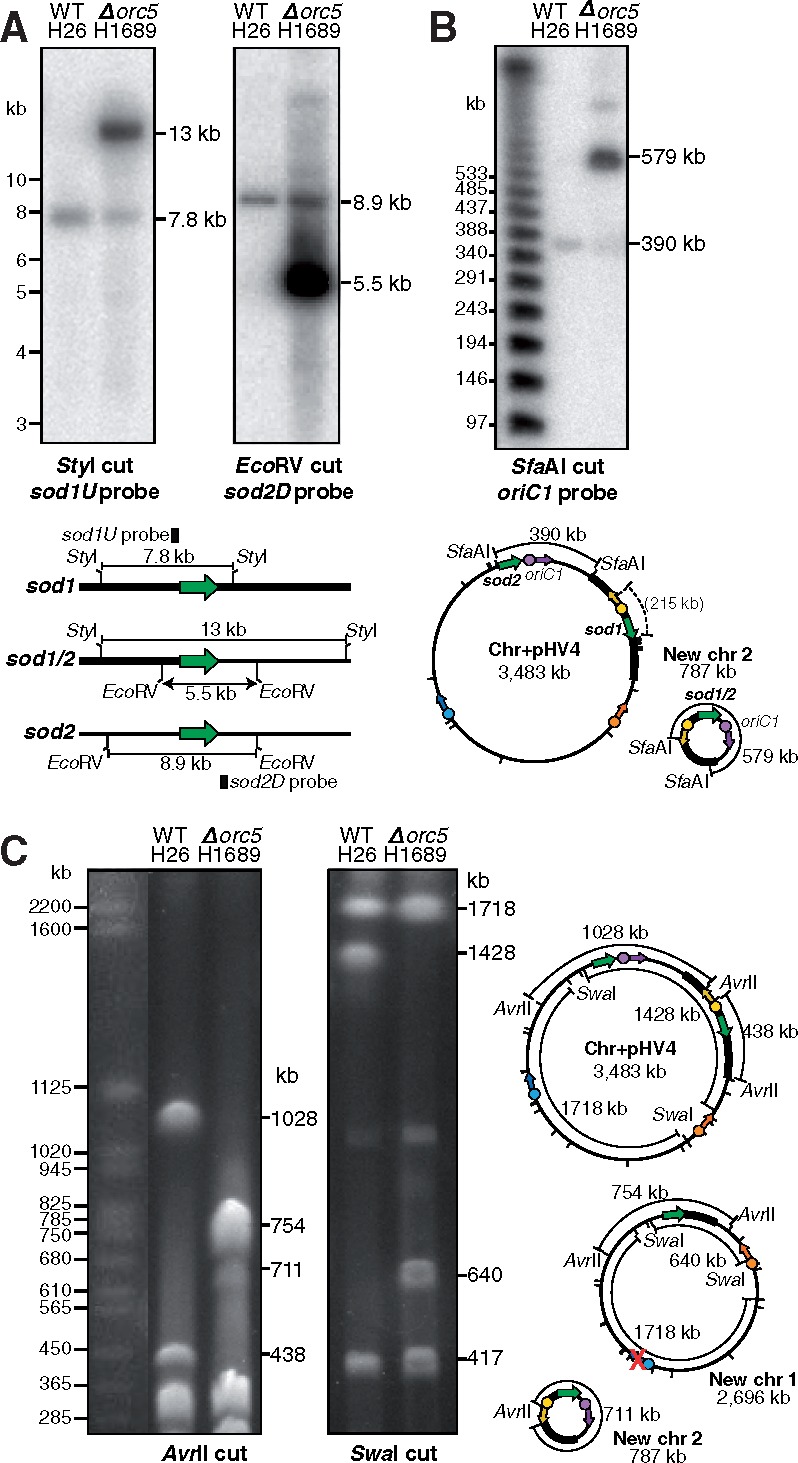
Genome architecture of the Δorc5 strain is polymorphic. (A) Southern blot conforming location of breakpoints of genome rearrangement in Δorc5 strain. Genomic DNA of WT H26 and Δorc5 H1689 was digested with StyI or EcoRV and probed with sequences adjacent to sod1 or sod2, respectively. A WT-sized band is present in the Δorc5 lanes. (B) Southern blot of PFGE confirming relocation of oriC1 to new chr 2 in Δorc5 strain. SfaAI-digested DNA of WT H26 and Δorc5 H1689 strains was probed with sequences adjacent to oriC1. Relevant SfaAI sites are indicated on the maps, the new chr 1 does not hybridize with oriC1 (map not shown). A faint 390 kb WT-sized band is present in the Δorc5 lane. (C) PFGE confirming new genome architecture of Δorc5 strain. Genomic DNA of WT H26 and Δorc5 H1689 was digested with AvrII or SwaI. Relevant AvrII and SwaI sites are indicated on the outside and inside of chromosome maps, respectively. The 417 bp SwaI fragment is found on pHV3 (not shown), which is not affected by the genome rearrangement.
