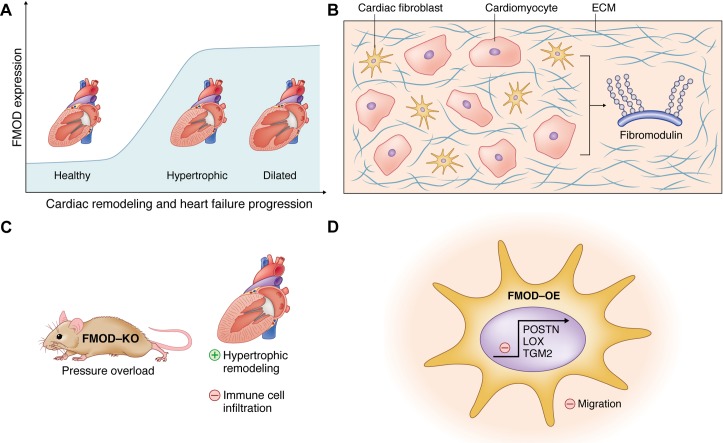
Fig 7. Schematic illustration of the proposed role of fibromodulin in the failing heart.
The schematic illustrates the main findings of our study. (A) Fibromodulin (FMOD) expression in the heart is increased during cardiac remodeling and heart failure progression in patients and mice. (B) FMOD is an extracellular matrix (ECM) proteoglycan produced by both cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts, the two major cell types in the heart. (C) FMOD knock-out (FMOD-KO) mice show mildly exacerbated hypertrophic remodeling of the heart with attenuated infiltration of leukocytes in response to experimental pressure overload. (D) FMOD overexpression (FMOD-OE) in cultured cardiac fibroblasts decreases their migratory capacity and reduces the expression of fibrosis-related ECM molecules such as periostin (POSTN), transglutaminase 2 (TGM2), and the collagen-cross linking enzyme lysyl oxidase (LOX). Thus, we propose that FMOD has anti-hypertrophic, anti-fibrotic and pro-inflammatory effects in the pressure-overloaded heart.