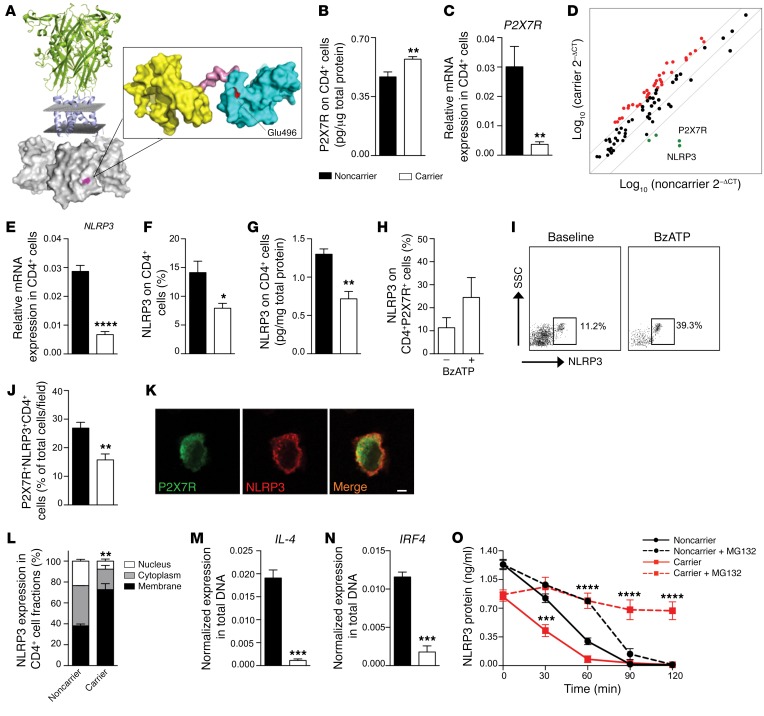
Figure 2. A C-terminal P2X7R mutation dysregulates NLRP3 expression and function in human CD4+ T cells.
(A) A 3D representation of the full-length structure of P2X7R, highlighting the putative location of the P2X7R mutation in the C-terminal intracellular portion. (B and C) Quantification of P2X7R total protein (B, ELISA, n = 3) and of P2X7R mRNA (C, qRT-PCR, n = 10) on CD4+ T cells of carrier and noncarrier patients. Samples were run in duplicate (B) or in triplicate (C) and normalized to expression level of β-actin (ACTB). (D) Transcriptome profiling of immune-relevant genes (see also Supplemental Table 3) examined in CD4+ T cells of carrier and noncarrier cardiac-transplanted patients (n = 5). (E–G) Expression of NLRP3 mRNA using qRT-PCR (E) and NLRP3 protein using flow cytometry (F) and ELISA (G) in CD4+ T cells of carrier and noncarrier patients (n = 5). (H and I) Flow cytometric expression of NLRP3 on CD4+P2X7R+ cells of carrier patients stimulated with BzATP (n = 5). (J) Percentage of P2X7R+NLRP3+ cells of carrier and noncarrier patients analyzed by immunofluorescence (Figure 1C and Supplemental Figure 2G) (n = 3). (K) Confocal microscopy analysis (×100 original magnification) of P2X7R (green) and NLRP3 (red) coexpression in CD4+ T cells of carrier patients (n = 3). Scale bar: 5 μm. (L) Subcellular localization of NLRP3 in CD4+ T cells of carrier and of noncarrier patients (n = 3). (M and N) IL-4 (M) and IRF4 (N) gene expression detected after ChIP with NLRP3 antibody in CD4+ T cells. (n = 3). (O) Quantification of NLRP3 protein measured in CD4+ T cells treated with the ubiquitin/protease inhibitor MG132 (n = 3). Bars represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; Student’s t test or 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test.