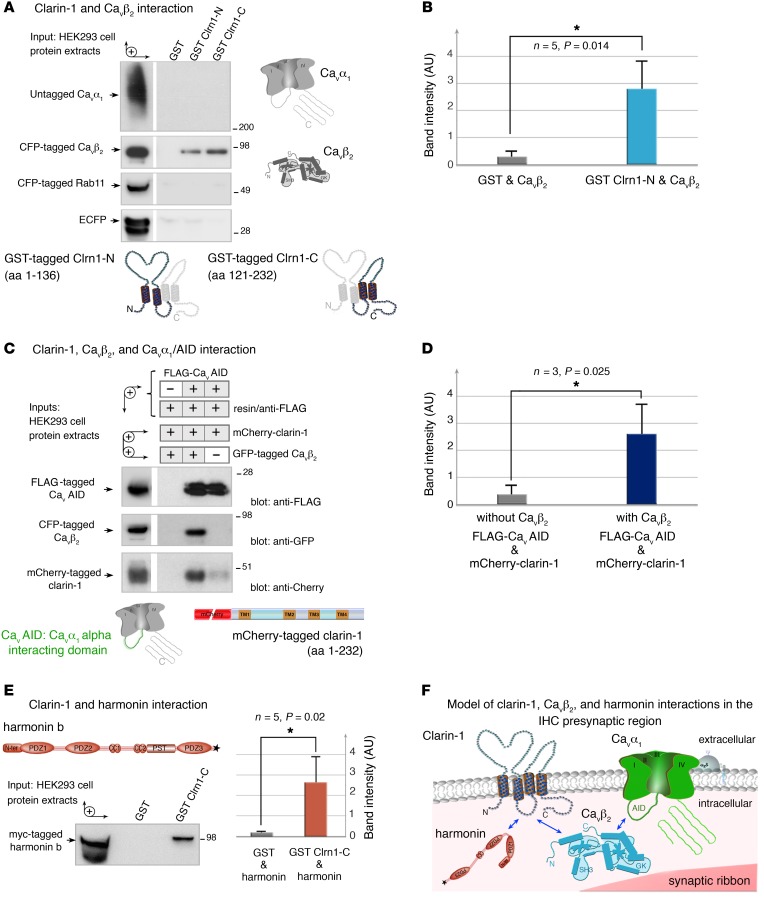
Figure 11. Interactions between clarin-1, the Cav1.3 channel complex, and harmonin.
(A and B) The GST-tagged clarin-1 N-terminal region (Clrn1-N) and C-terminal region (Clrn1-C) bind to CFP-tagged CaVβ2 produced in HEK293 cells, whereas GST alone does not. No binding is detected with the untagged CaVα1, CFP-tagged Rab11, or ECFP alone. (B) The bar chart indicates the significant interaction between clarin-1 and CaVβ2 (n = 5, *P < 0.05; unpaired Student’s t test). (C and D) In a coimmunoprecipitation assay, anti-FLAG M2 resin was incubated with HEK293 cells coproducing FLAG-tagged CaVAID, mCherry-tagged clarin-1, and CFP-tagged CaVβ2, or mCherry-tagged clarin-1 and CFP-tagged CaVβ2. (D) Significant binding between CaVAID and clarin-1 is observed only in the presence of CaVβ2 (n = 3, *P < 0.05; unpaired Student’s t test). (E) GST-tagged Clrn1-C binds to myc-tagged harmonin b, whereas GST alone does not. The bar chart shows the significant interaction between clarin-1 and harmonin (n = 5, P < 0.05; unpaired Student’s t test). (F) Schematic representation of a synaptic active zone summarizing the interactions between clarin-1, the Ca2+ channel subunits CaVβ2 and CaVα1, and harmonin (see uncut gels in supplemental material).