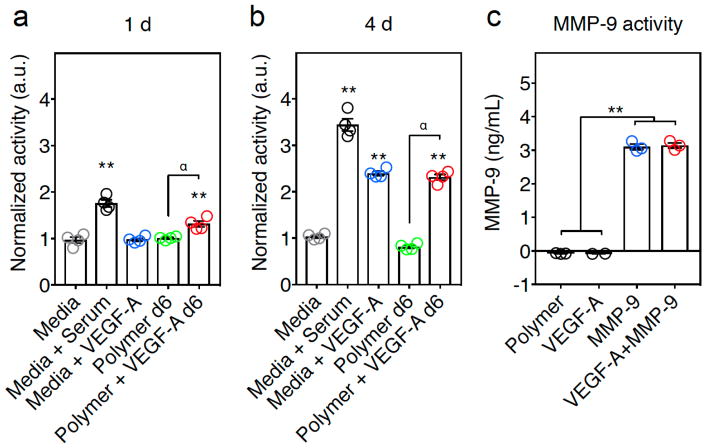
Figure 2.
VEGF-A and MMP-9 released from polymer hydrogels are biologically active. (a, b) In vitro measurement of VEGF-A activity assay on hMVECs. (a) After 1 day of exposure, hMVECS exposed to Polymer+VEGF-A supernatant had more activity than hydrogel alone (Polymer) supernatant. (α, p ≤ 0.01). The 6-day Polymer+VEGF-A supernatant and control containing Media+Serum showed significantly higher than Media alone (**, p ≤ 0.01). (b) After exposure in culture for 4 days, the 6-day Polymer+VEGF-A supernatant showed similar outgrowth to the controls containing Media+Serum and Media+VEGF-A and significantly higher than Media alone (**, p ≤ 0.01) or the day 6 Polymer alone supernatant group (α, p ≤ 0.01) (ANOVA analysis showed at 1d and 4d F = 72.68 and 404.5, p ≤ 0.0001 and 0.0001, respectively. Post-hoc Tukey HSD test shows that Polymer+VEGF-A at 1d and 4d was statistically significant compared to the Polymer group (α, p ≤ 0.01), and ** indicates p ≤ 0.01 as compared to the Media control, error bars are SEM, n=4). (c) MMP-9 activity after release from the hydrogel. Polymer with MMP-9 (MMP-9) or VEGF-A+MMP-9 had significantly more activity than the controls of Polymer alone or polymer with VEGF-A (VEGF-A), (ANOVA analysis showed F = 810 and p ≤ 0.0001. Post-hoc Tukey HSD test showed statistical significance, ** indicates p ≤ 0.01, error bars are SEM, n=3).