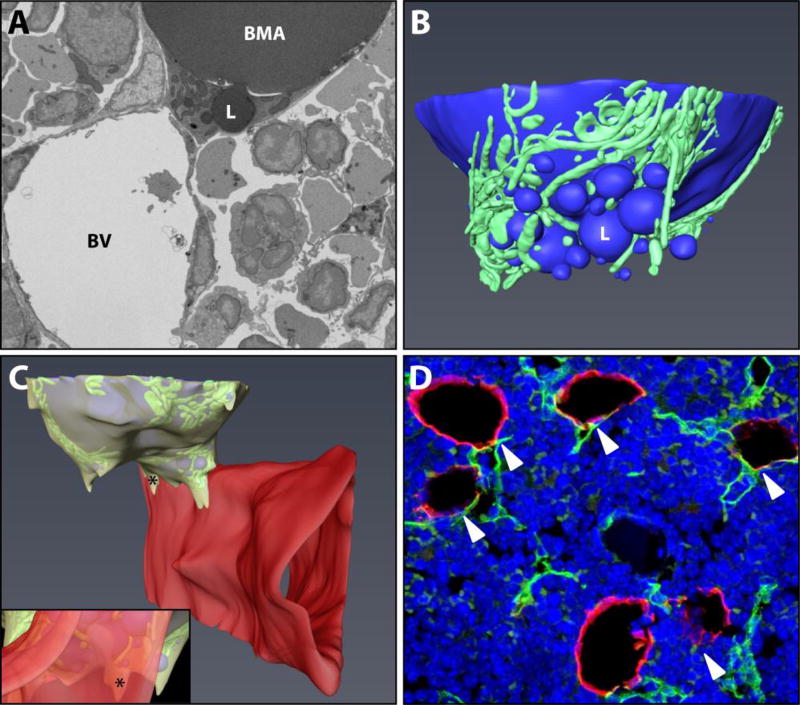
Figure 1. Basic ultrastructure and vascular connections of the tibial bone marrow adipocyte.
(A) The ultrastructure of a bone marrow adipocyte from the proximal tibial metaphysis of a wild type C57BL/6J mouse was reconstructed from a FIB-SEM dataset containing 1,329 independent images (Dataset #1). BMA = bone marrow adipocyte, BV = blood vessel, L = lipid droplet. (B) The reconstruction revealed a large lipid droplet and a multitude of smaller lipid droplets (blue). The smaller lipid droplets were enmeshed by a dense network of mitochondria (green). (C) The majority of the smaller lipid droplets were polarized toward a sinusoidal blood vessel (red). The adipocyte cytoplasm (yellow) was immediately adjacent to the endothelial cell of the blood vessel. Inset: view from the interior of the blood vessel toward the adipocyte. * = cytoplasm of BMA. Imaging location: C57BL/6J mouse, proximal tibia. (D) Consistent with the EM study, immunohistochemical analysis of the bone marrow shows that perilipin positive bone marrow adipocytes (red) consistently make at least one connection with an endomucin positive blood vessel (green, arrowheads). DAPI in blue. Representative image from an 8-month-old male C57BL/6J mouse (N = 3). See also Supplementary Video 1.