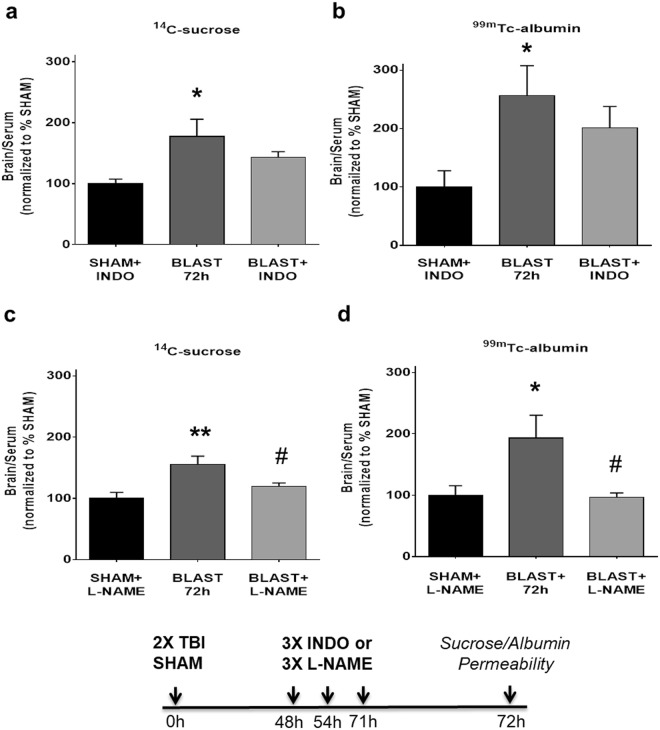
Figure 4.
Nitric oxide synthase inhibition blocks delayed blood-brain barrier disruption after blast. (a) At 72 h after 2X blast, a significant increase in 14C-sucrose, (b) and 99mTc-albumin was measured in whole brains compared to sham controls treated with INDO (5 mg/kg; ip). (a) No significant differences in 14C-sucrose, (b) or 99mTc-albumin were observed when INDO was administered after blast. (c) A significant increase in 14C-sucrose, (d) and 99mTc-albumin was also observed in whole brain at 72 h after 2X blast compared to L-NAME treated sham controls. (c) L-NAME administration (10 mg/kg; ip) significantly attenuated a blast-induced increase in 14C-sucrose, (d) and 99mTc-albumin. One-way ANOVA post hoc Newman-Keul’s. Values represent mean ± SEM; n = 5. (*p ≤ 0.05 vs sham + L-NAME; #p ≤ 0.05 vs blast + vehicle; **p ≤ 0.01 vs sham + INDO).