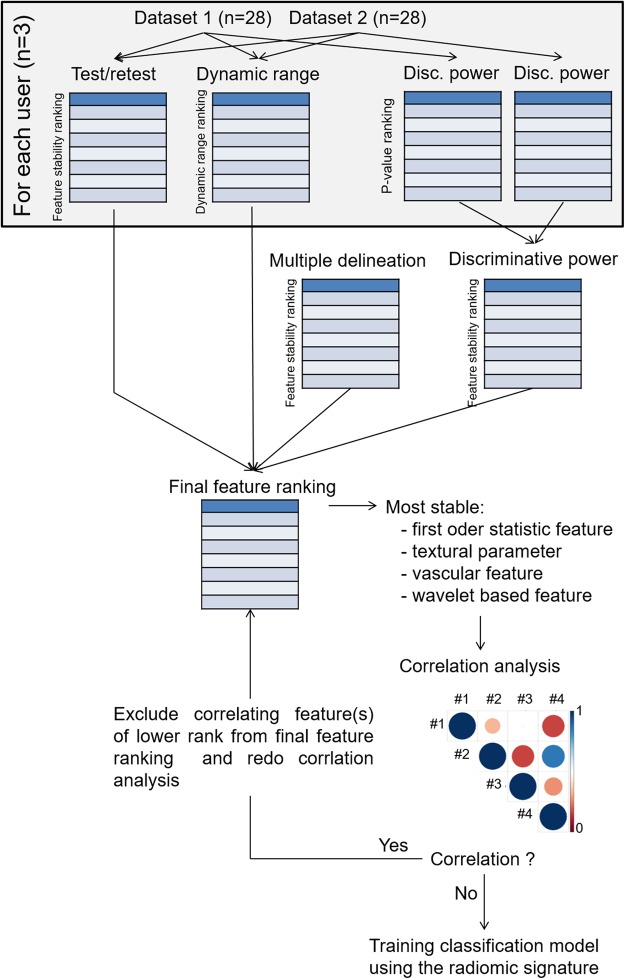
Figure 3.
Workflow of feature selection process. Two datasets were used to determine the feature stability by performing a Test/Retest measurement, and ranking all extracted features with respect to their stability in between the two measurements. The dynamic range in relation to the variability of the measurement was assessed and ranked from high to low. To identify features, which are user independent, the two datasets of each user were combined, and tested for their stability in between the different users. Furthermore, the Kruskal-Wallis test was performed on each dataset to generate a discriminative power ranking. The Test/Retest, dynamic range, multiple delineation and discriminative power rankings were applied to compute a final ranking of all extracted imaging features. The most stable features of each imaging biomarker class were selected to compose the radiomic signature. A correlation analysis was performed to exclude correlating features. The final radiomic signature consisted of four features which were not correlating, one from each imaging biomarker class.