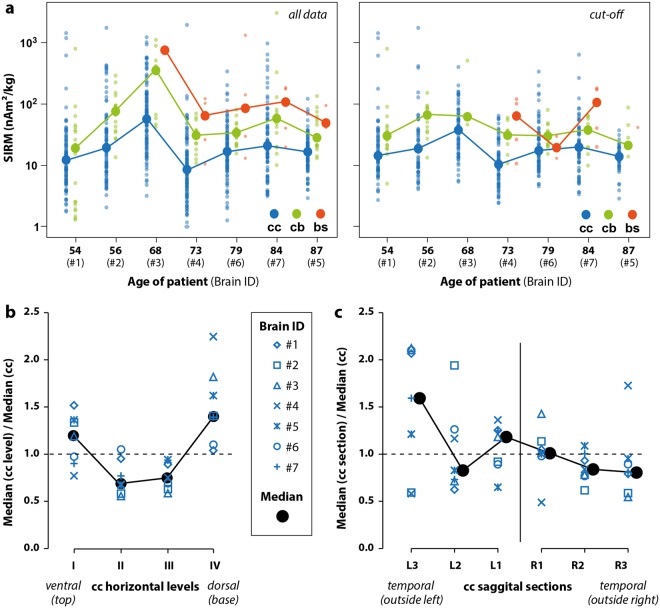
Figure 3.
(a) Median, mass normalized, saturation isothermal remanent magnetization (SIRM) values of the cerebral cortex (cc), cerebellum (cb) and brain stem (bs) for each of the seven brains classified according to the person’s age using all data (left) and after using the cut-off method (right). Individual data points are small circles; medians are large circles. (b) Median SIRM of each level (I-IV) in the cerebral cortex divided by the median SIRM of the entire cerebral cortex for each individual brain using the cut-off method. Horizontal level IV (ventral, basal) in each brain was systematically more magnetic than the median value and levels II and III were less magnetic. (c) Median SIRM of each sagittal section of the cerebral cortex segregated by hemisphere (left, L and right, R) divided by the median SIRM of the entire cerebral cortex for each individual brain (cut-off method). The left hemisphere had higher magnetization in general and more variability, with the temporal (outside, L3) area generally being more magnetic whereas the temporal region of the right side (R3) was less magnetic. Median magnetizations between the left and right hemispheres were statistically significantly different from each other (p = 0.047).