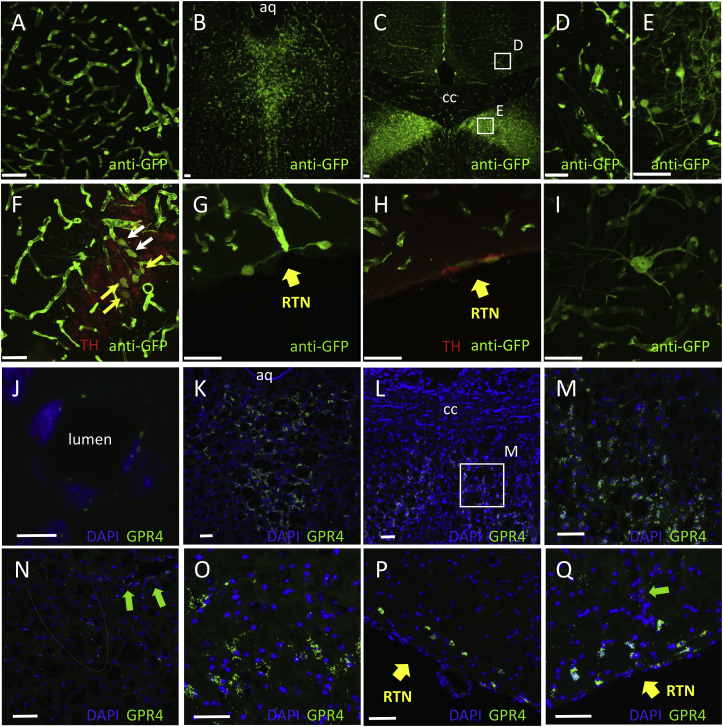
Fig. 1.
GPR4 expression in the mouse brain.
A-I. Fluorescent immunohistochemistry of GPR4-CRE-STOP-EGFP mouse brain slices using antibodies against EGFP (anti-GFP) and TH (marker of catecholaminergic neurones). Unless indicated otherwise, scale bars are 50μm.
A. GPR4 expression in blood vessels was prominent throughout the whole brain (see all panels).
B. Strong and wide-spread GPR4 expression in dorsal raphe nucleus neurones.C. GPR4 expression in neurones of the lateral septum.
D, E. Higher magnification images from areas indicated in panel C.
F. In the locus coeruleus (A6 cell group) GPR4 expression was detected in neurones, some of which were TH-positive (yellow arrows) or TH-negative (white arrows).
G. Ventral edge of the medulla oblongata at the level of RTN. A few RTN neurones could be detected in some sections. Less than 10 EGFP-positive cells per animal were found.
H. Some of the sections at RTN level were double-stained for TH, but TH-positive cells were EGFP-negative and probably belonged to the C1 cell group.
I. Scattered neurones of unclear phenotype were sporadically detected throughout the whole brain.
J-Q – Results of RNAscope FISH.
J. A blood vessel, scale bar 10μm
K. Dorsal raphe
L. lateral septum
M. Lateral septum, magnified from L, scale bar 10μm
N. Locus cortuleus, boundaries highlighted by the dotted line
O. C1 cell group
P and Q: RTN
Green arrows in N and Q – blood vessels
aq – aqueduct; CC – corpus collosum; RTN – retrotrapezoid nucleus
See Supplement for the large scale versions of some of the images.