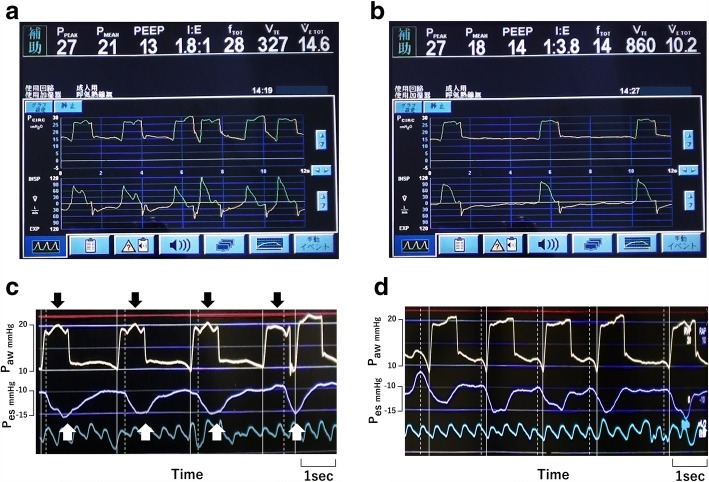
Fig. 1.
a, b Airway pressure (Paw, top) and flow (bottom) waveforms over time during pressure assist-control ventilation. c, d Paw (top) and esophageal pressure (Pes, bottom) tracings. Solid lines indicate the start of machine cycles and dotted lines indicate the start of neural efforts. c All cycles (black arrows), occurring at 22 breaths/min, more than the set frequency, were auto-triggered rather than time-cycled breaths. White arrows indicate entrained breaths (reverse triggering) triggered by auto-triggered breaths. At the fourth breath, owing to a second machine cycle that was triggered by the entrained breath, “breath stacking” occurred. d After preventing auto-triggering by increasing ETT cuff pressure, neural efforts preceded machine cycles while the order of machine cycle and neural effort was reversed in c