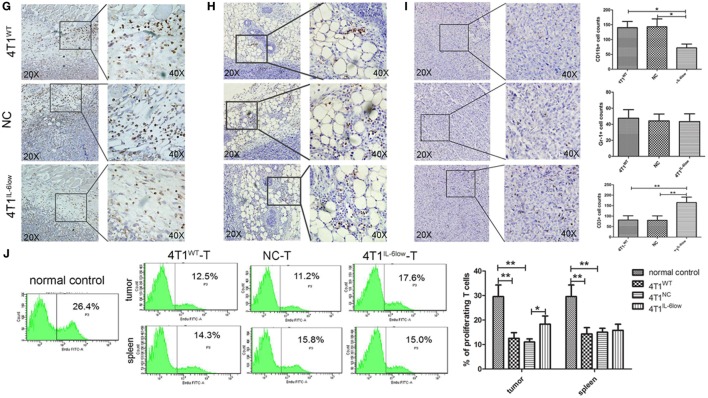
Figure 3.
Tumor-derived interleukin-6 (IL-6) promotes the accumulation of CD11b+Gr-1−F4/80−MHCII− early-stage MDSCs (e-MDSCs) in tumors. Infiltrated CD45+ cells were gated. (A) The percentage of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in normal spleen, tumors, and spleens resulting from 4T1 mammary cancer cells detected by flow cytometry. (B) The percentage of the indicated cell subsets in tumors and spleens from mice bearing different IL-6-expressing tumors was determined by flow cytometry. CD11b+Gr-1− e-MDSCs from spleens and tumors were isolated, and the percentage of CD11b+Gr-1−F4/80+MHCII− cells and CD11b+Gr-1−F4/80−MHCII+ cells in spleens (C) and tumors (D) was determined using flow cytometry. (E) The correlation analysis between tumor volumes and the percentage of tumor-infiltrating CD11b+Gr-1−F4/80−MHCII− e-MDSCs or CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs (R2 = 0.4491 vs. R2 = 0.1482, P < 0.001, P < 0.05). (F) Correlation analysis between lung metastatic nodules and the percentage of tumor-infiltrating CD11b+Gr-1−F4/80−MHCII− e-MDSCs or CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs (R2 = 0.3587 vs. R2 = 0.1342, P = 0.0001, P < 0.05). Infiltration of CD11b+ cells (G), Gr-1+ cells (H), and CD3+ T cells (I) in tumors expressing different amounts of IL-6 was determined by immunohistochemistry. Five high-power fields (400× magnification) for each tissue section were selected randomly for histology evaluation. (J) BrdU (50 mg/kg) was injected by tail vein separately to mice bearing 4T1WT, 4T1NC, or 4T1IL-6low tumors, and proliferative T cells labeled with BrdU in tumors and spleens were detected. T cells in spleen of normal mice were used as control (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.0001).