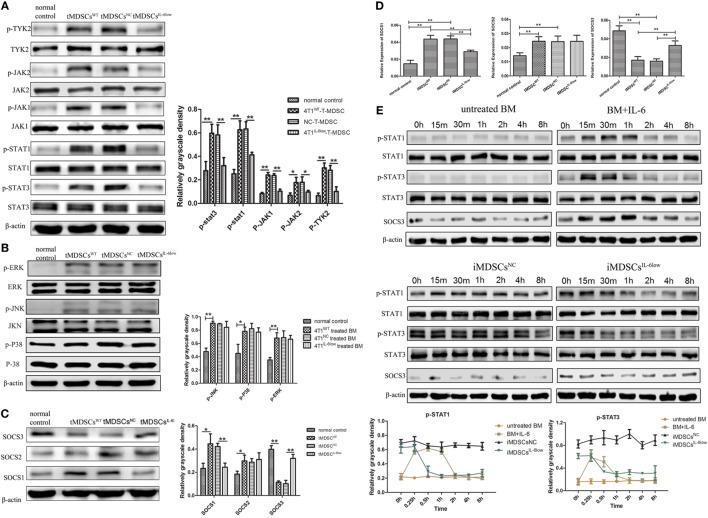
Figure 6.
Interleukin-6 (IL-6)-mediated suppressed expression of SOCS3 resulting in the hyperactivation of the JAK/STAT pathway in CD11b+Gr-1− early-stage MDSCs (e-MDSCs). Western blotting was performed to detect the JAK/STAT (A) and MAPK (B) on the whole-cell extracts of primary CD11b+Gr-1− e-MDSCs isolated from different IL-6-expressing tumors. (C) The protein expression of SOCS1–3 in primary CD11b+Gr-1− e-MDSCs. (D) The mRNA of SOCS1–3 in primary CD11b+Gr-1− e-MDSCs was examined by RT-PCR. (E) Bone marrow (BM) cells were treated with 4T1NC and 4T1IL-6low separately to induce iMDSCsNC and iMDSCsIL-6low. The activation status of the JAK/STAT pathway downstream of IL-6 signaling in induce MDSCs (iMDSCs) was detected at different time point. BM cells exposed to IL-6 (40 ng/mL) for 15 min were as control. The levels of phosphorylated JAK1 (p-JAK1), p-JAK2, p-TYK2, p-STAT1, p-STAT3, p-P38, p-ERK, and p-JNK were compared using the density ratio of phosphorylated protein to total protein. The levels of the suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) protein were compared using the density ratio of the indicated protein to β-actin (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01).