Figure 1.
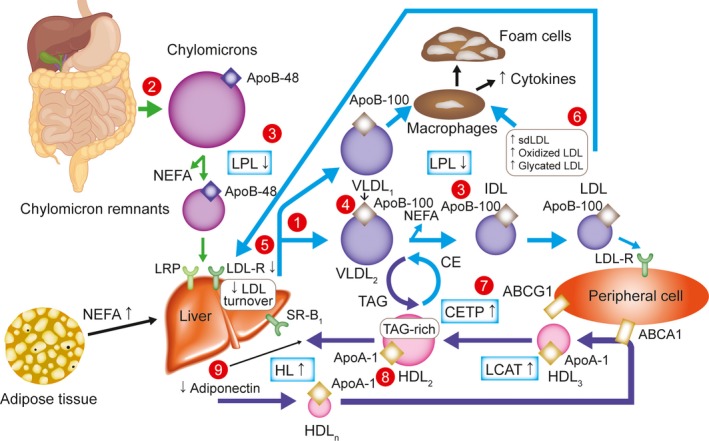
Overview of lipid abnormalities in T2DM.32 Triacylglycerols (hypertriglyceridemia, qualitative and kinetic abnormalities): (1) increased VLDL production (mostly VLDL1); (2) increased chylomicron production; (3) reduced catabolism of both chylomicrons and VLDLs (diminished LPL activity); (4) increased production of large VLDL (VLDL1), preferentially taken up by macrophages; LDL (qualitative and kinetic abnormalities); (5) reduced LDL turnover (decreased LDL B/E receptors); (6) increased number of glycated LDLs, small, dense LDLs (TAG‐rich) and oxidized LDLs, which are preferentially taken up by macrophages; HDL (low HDL‐C, qualitative and kinetic abnormalities); (7) increased CETP activity (increased transfer of triacylglycerols from TAG‐rich lipoproteins to LDLs and HDLs); (8) increased TAG content of HDLs, promoting HL activity and HDL catabolism; (9) low plasma adiponectin favoring the increase in HDL catabolism. ABCA1 indicates ATP‐binding cassette A1; ABCG1, ATP‐binding cassette G1; Apo, apolipoprotein; CE, cholesterol ester; CETP, CE transfer protein; HDL, high‐density lipoprotein; HDL‐C, HDL cholesterol; HDLn, nascent HDL; HL, hepatic lipase; LCAT, lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase; LDL, low‐density lipoprotein; LDL‐R, LDL receptor; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; LRP, LDL receptor‐related protein; NEFA, nonesterified fatty acid; sdLDL, small, dense LDL; SR‐B1, scavenger receptor B1; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; TAG, triacylglycerol; VLDL, very low‐density lipoprotein.
