Figure 3.
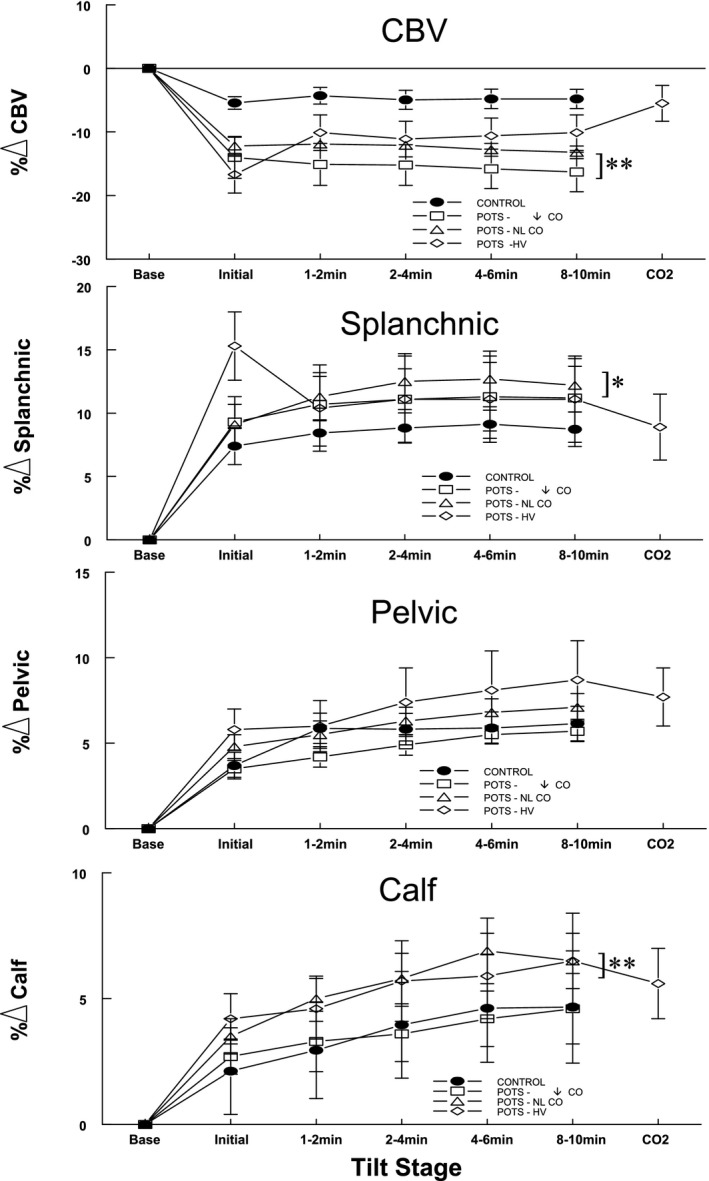
Regional blood volume data averaged over all groups for subjects with postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and control subjects. The percentage change of central blood volume was reduced for all POTS groups before administering CO 2. Splanchnic blood volume in POTS‐hyperventilation (HV) increased, whereas central blood volume (CBV) reciprocally decreased, during the initial period. Splanchnic blood volume in all POTS groups exceeded control. Increased pelvic volume in POTS groups did not reach significance, although calf volume was significantly larger than control for POTS–normal CO (POTS‐NL CO) and POTS‐HV, but not for POTS‐↓CO (decreased CO without hyperventilation). After administration of supplemental CO 2, central and regional blood volumes became similar in subjects with POTS‐HV and control subjects. *P<0.01, **P<0.001.
