Figure 2.
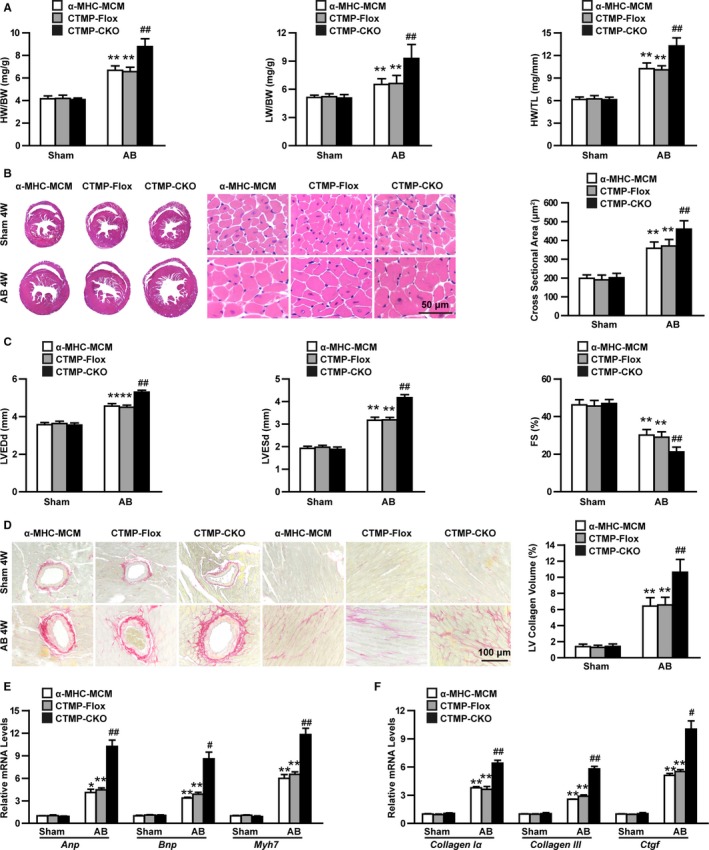
Cardiac‐specific carboxyl‐terminal modulator protein (CTMP) deficiency exacerbates pathological cardiac hypertrophy induced by aortic banding (AB). A, The ratios of heart weight (HW)/body weight (BW), lung weight (LW)/BW, and HW/tibia length (TL) in different genotypic mice (ɑ‐major histocompatibility complex–MerCreMer [ɑ‐MHC‐MCM], CTMPloxP/loxP [CTMP‐Flox], and cardiac‐specific knockout of CTMP [CTMP‐CKO]) 4 weeks (4W) after sham or aortic banding (AB) surgery (n=11–13 mice per group). B, Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining of hearts from each group (n=5–6 mice per group; bar=50 μm), and statistical results for the cardiomyocyte cross‐sectional area (n>100 cells per group). C, Quantitative analysis of left ventricular (LV) end‐diastolic diameter (LVEDd), LV end‐systolic diameter (LVESd), and fractional shortening (FS) in each group 4W after AB surgery (n=11–13 mice per group). D, Representative images of picrosirius red staining of hearts from each group (n=6 mice per group; bar=100 μm), and statistical results for fibrotic areas in each group (n>30 fields per group). E and F, Real‐time polymerase chain reaction analyses of hypertrophic (E) and fibrotic (F) markers in each group (n=4 per group). *P<0.05 or **P<0.01 vs ɑ‐MHC‐MCM sham or CTMP‐Flox sham; # P<0.05 or ## P<0.01 vs ɑ‐MHC‐MCM AB or CTMP‐Flox AB (A through F) by Tamhane's T2 analysis (A, B, and D‐F [Collagen III and Ctgf]) or Bonferroni post hoc analysis (C and F [Collagen Iα]).
