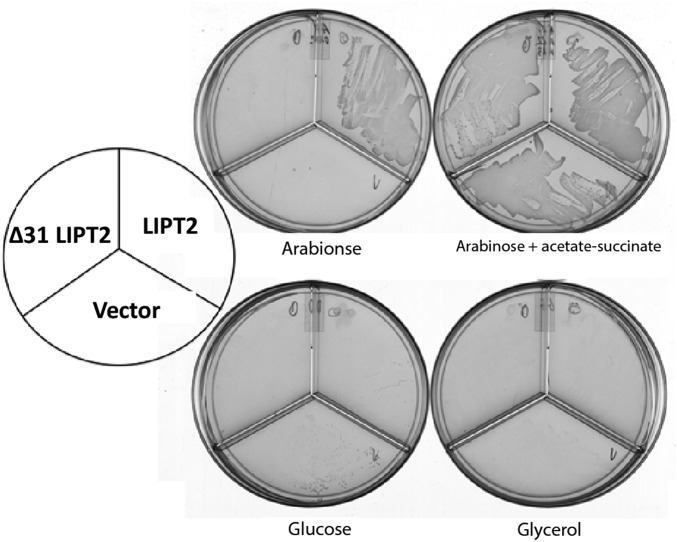
Fig. 8.
Complementation of the ∆lipB deletion of E. coli strain QC146 by expression of human LIPT2. Synthetic genes encoding either the full-length human LIPT2 or a derivative that lacked the first 31 residues (∆31, a methionine codon replaced residue 31 to permit translation) were inserted into vector pBAD322A as in Fig. 6 to give plasmids pCY1110 and pCY1108, respectively. The plasmids were introduced into strain QC146 (∆lipB ∆lplA) (75), and transformants were streaked onto plates containing 0.02% arabinose or another carbon source as given in Fig. 6. Note that, unlike the mouse LIPT2, 0.2% arabinose gave rapid growth, but growth soon halted, suggesting high-level expression of human LIPT2 is toxic.