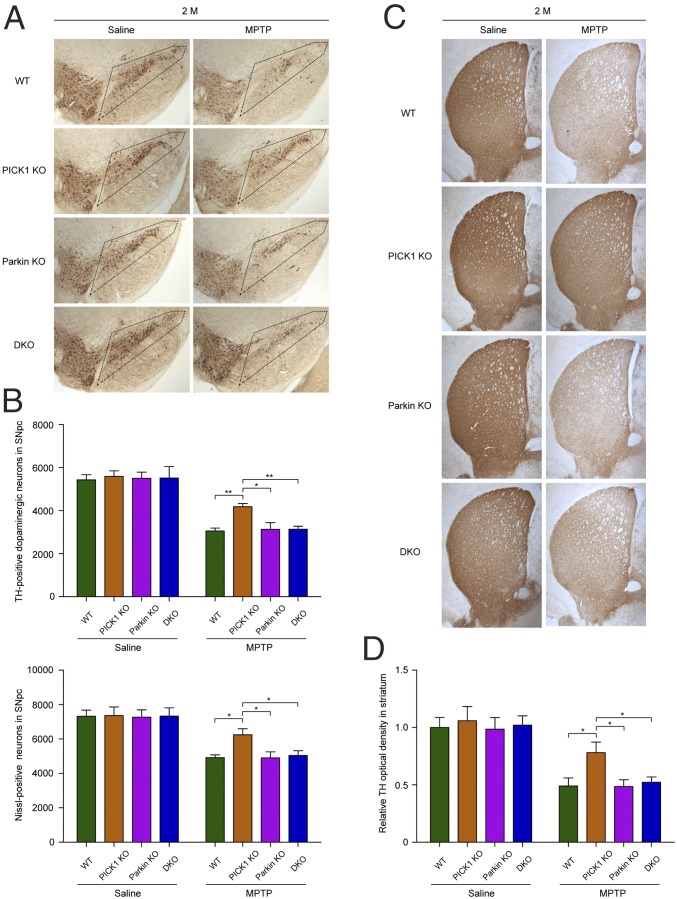
Fig. 5.
Young PICK1 KO mice are resistant to MPTP-induced toxicity. (A) Immunohistochemical analysis of dopaminergic neurons from young (2-mo-old) mice administered saline or MPTP. The boxed regions indicate the location of the SNpc. (B) Quantification of TH- and Nissl-positive neurons in the SNpc. For TH staining: saline: WT, n = 9; PICK1 KO, n = 7; Parkin KO, n = 10; DKO, n = 6. MPTP: WT, n = 8; PICK1 KO, n = 9; Parkin KO, n = 8; DKO, n = 10. n = 6 per genotype for Nissl staining. (C) TH immunohistochemistry of the striatum. (D) Quantification of OD of TH in striatum. Saline: WT, n = 9; PICK1 KO, n = 7; Parkin KO, n = 10; DKO, n = 6. MPTP: WT, n = 8; PICK1 KO, n = 9; Parkin KO, n = 8; DKO, n = 10. The mice were killed 5 d after last dosage of MPTP administration. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.