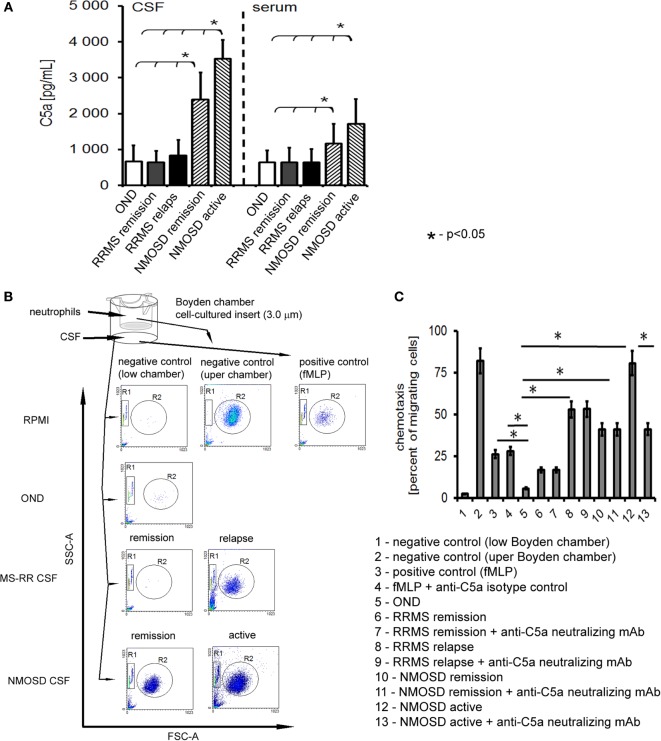
Figure 1.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) derived from neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) patients induces chemotaxis of healthy control neutrophils by C5a. (A) NMOSD is characterized by the high concentration of C5a in CSF and serum compared with remitting–relapsing multiple sclerosis (RRMS) or other neurological disorders (OND). The bars represent the means ± SD. (B) NMOSD CSF possesses chemotaxis properties independently of whether it was collected in the active or remission stage of the disease, while RRMS CSF possesses chemotaxis activity during disease relapse only. As a negative control, RPMI and neutrophils from upper chamber were used; as a positive control, fMLP was used. The example of one of four independent experiments. (C) NMOSD CSF chemotaxis properties are mainly dependent on the classical pathway of complement activation, as C5a neutralization inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis in NMOSD patients in oppose to RRMS CSF. Data are presented as the mean rates of cell migration ± SD from four independent experiments.