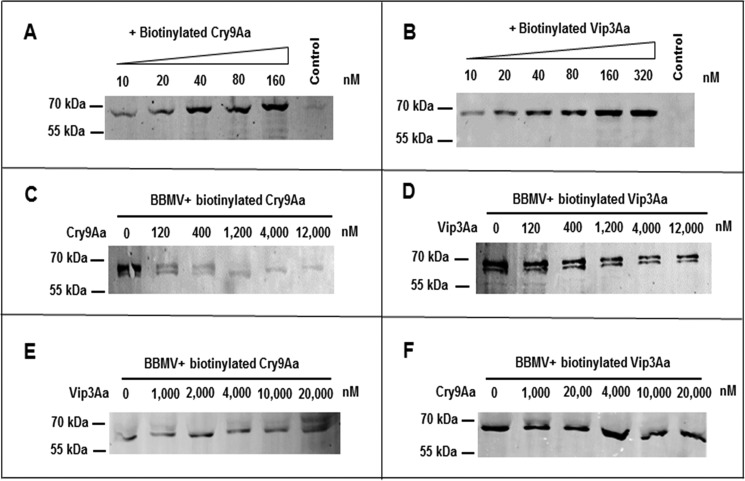
Figure 1.
Binding assay of Cry9Aa and Vip3Aa toxins to BBMVs from C. suppressalis. A and B, saturation binding assays were done using increasing concentrations of Cry9Aa and Vip3Aa to BBMVs, respectively, showing that binding of these toxins to the BBMVs is saturable. A control of the highest concentration of biotinylated toxins without BBMVs was included in this figure, showing that the biotinylated toxins did not precipitate in the absence of membranes. C and D, homologous binding competition assays of 40 nm biotinylated Cry9Aa or biotinylated Vip3Aa to BBMVs in the presence of increasing concentrations of the same unlabeled toxin were performed, showing that both toxins were competed by their corresponding unlabeled toxin. E and F, heterologous binding competition assays of 40 nm biotinylated Cry9Aa or Vip3Aa to BBMVs performed in the presence of increasing concentrations of the other unlabeled toxin, showing that binding of biotinylated toxins could not be competed by the other unlabeled toxin.