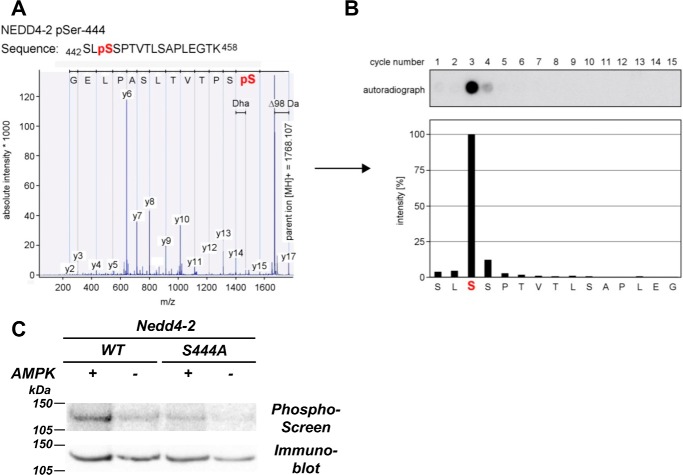
Figure 1.
AMPK phosphorylates xNedd4-2 at Ser-444. A, isolated phosphopeptides were derived from the HPLC system and subjected to MALDI-TOF MS for mass fingerprinting. Peptides with a mass shift of +80 Da (HPO3) were then selected for MS/MS, and phosphorylation was confirmed by a neutral loss of −98 Da (H3PO4 or HPO3 and H2O) during fragmentation. B, solid-phase sequencing of the radiolabeled peptides was performed to verify the phosphosite. Liberated single amino acids were collected and spotted onto a diethylaminoethyl cellulose membrane after each cycle of N-terminal Edman degradation. Autoradiography was then conducted to detect the respective phosphorylated residues. C, S444A reduced the level of AMPK-mediated phosphorylation of xNedd4-2. FLAG-tagged xNedd4-2 (WT or S444A) constructs were transiently transfected into HEK293 cells, immunoprecipitated from cell lysates, and exposed to purified AMPK or buffer alone and [γ-32P]ATP. After SDS-PAGE and transfer to a nitrocellulose membrane, immunoblotting and phosphorimaging were performed on the same membrane.