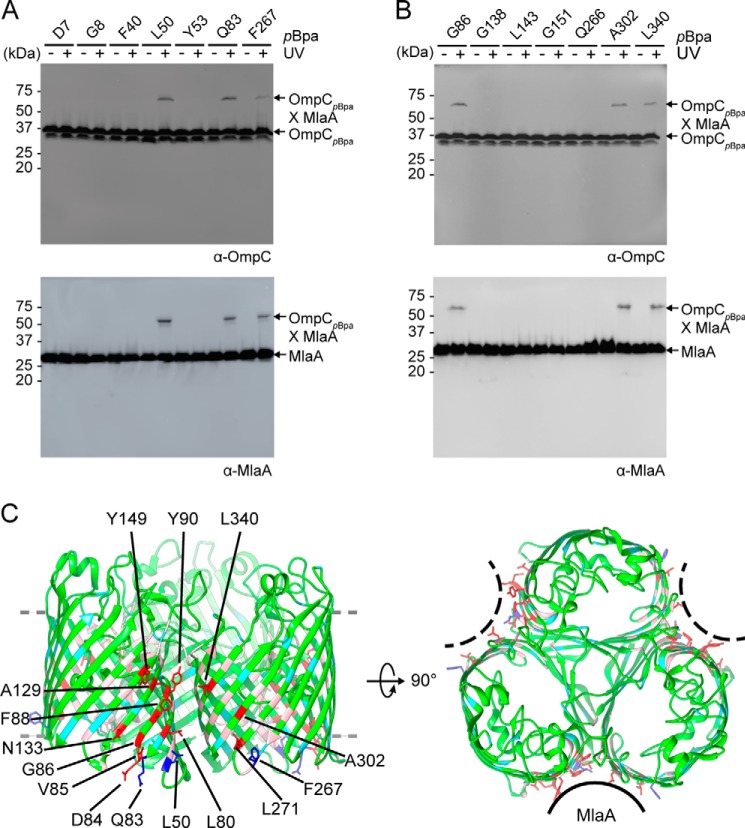
Figure 1.
MlaA binds at the dimeric interfaces of the OmpC trimer in vivo. A and B, representative immunoblots showing UV-dependent formation of cross-links between OmpC and MlaA in ΔompC cells expressing OmpC substituted with pBpa at the indicated positions, selected in a global (A) or localized (B) search. C, side (left panel) and top (right panel) views of cartoon representations of the crystal structure of E. coli OmpC (Protein Data Bank code 2J1N) (18) with positions that cross-link to MlaA highlighted. Residues selected in the global search for MlaA interaction are colored cyan (no cross-links) and blue (sticks; cross-links detected), whereas those selected in the localized search are colored light pink (no cross-links) and red (sticks; cross-links detected). The OM boundary is indicated as gray dashed lines. MlaA binding sites are indicated as solid or dashed curves on the top-view representation. The figures were generated using the program Chimera (54).