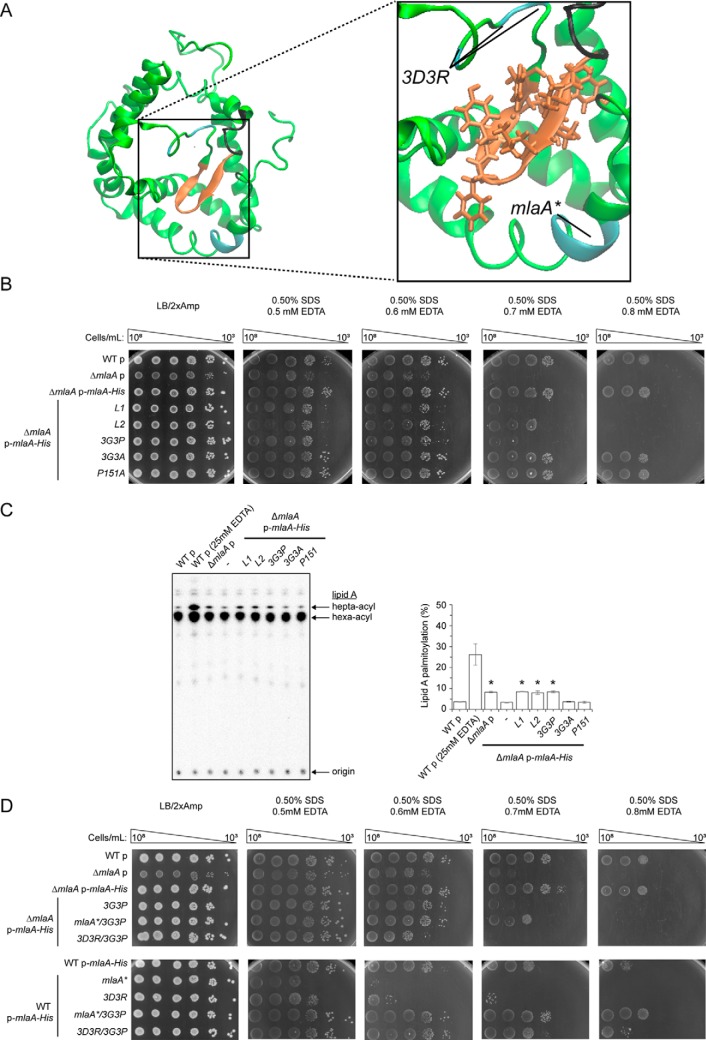
Figure 6.
Flexibility in a hairpin loop structure on MlaA adjacent to the hydrophilic channel is critical for function. A, a representative structure of MlaA from all-atomistic MD simulations (as in Fig. 3B) with the hairpin loop adjacent to the hydrophilic channel highlighted. In the expanded representation, the 3D3R and mlaA* mutations, the hairpin loop, and the glycine-rich region N-terminal to the loop are colored in cyan, orange, and black, respectively. Residues on the hairpin loop chosen for mutation are represented as sticks. The figures were generated using the program VMD (55). B, analysis of SDS/EDTA sensitivity of WT and ΔmlaA strains producing indicated MlaA loop variants from the pET23/42 vector (p). C, representative TLC/autoradiographic analysis of 32P-labeled lipid A extracted from exponential phase cultures of strains described in B. Equal amounts of radioactive material were spotted for each sample. The average percentages of palmitoylation of lipid A and the standard deviations were quantified from triplicate experiments and plotted on the right. For Student's t tests: *, p < 0.0005 compared with WT with empty vector. D, analysis of SDS/EDTA sensitivity of WT and ΔmlaA strains producing indicated MlaA variants from the pET23/42 vector (p).