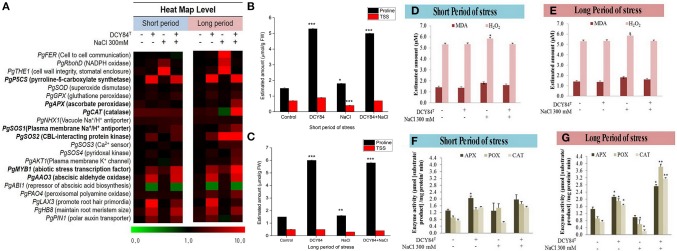
Figure 6.
Priming of DCY84T alleviates various biochemical changes caused by short- and long-term salinity stress. (A) Heat map of qRT-PCR results for salinity-responsive genes. The relative expression of ginseng genes was normalized using PgCYP as the housekeeping gene. Bold letters indicate significant fold change in relative expression from at least one kind of treatment. (B,C) Proline and total soluble sugar (TSS) levels of P. ginseng seedlings. (D,E) MDA and H2O2 levels of P. ginseng seedlings. Both assays were conducted using root tissue samples. (F,G) Antioxidant enzyme activity of P. ginseng seedlings. Data represent the mean of three biological replicates and were analyzed using the student t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001). Short period, 3 days of salinity stress; long period, 12 days of salinity stress.