Figure 1.
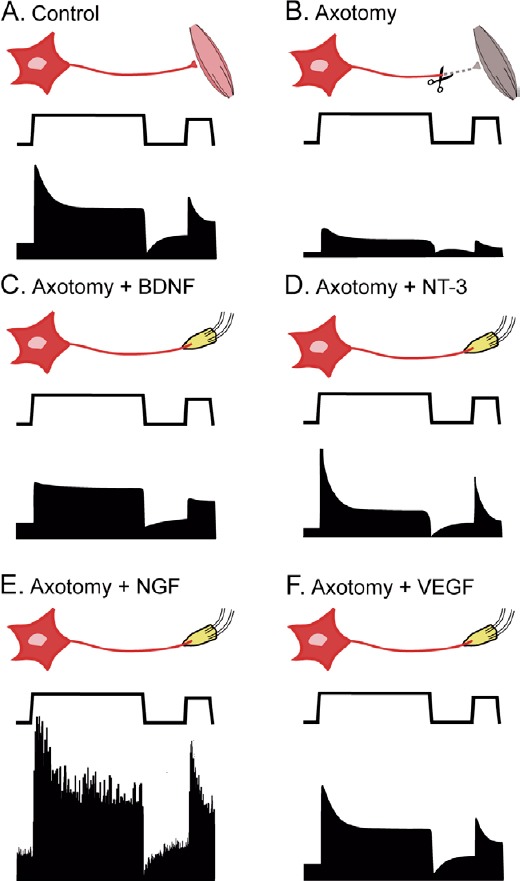
Schematic diagram comparing the results obtained after different neurotrophic factor administration on axotomized abducens motoneurons.
In each panel, from top to bottom: experimental situation, eye position, and associated firing rate. (A) Control motoneurons show a typical tonic-phasic discharge proportional to eye position and velocity. (B) Axotomy decreases the discharge, affecting both the tonic and the phasic components. (C) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) administration recovers essentially the tonic firing. (D) Neurotrophic-3 (NT-3) treatment restores basically the phasic activity. (E) Nerve growth factor (NGF) increases both the tonic and the phasic components as well as discharge variability over control values. (F) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) treatment completely recovers the firing pattern of axotomized motoneurons to control values.
