Figure 4. AGE-BSA-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis is mediated through PKCδ activation.
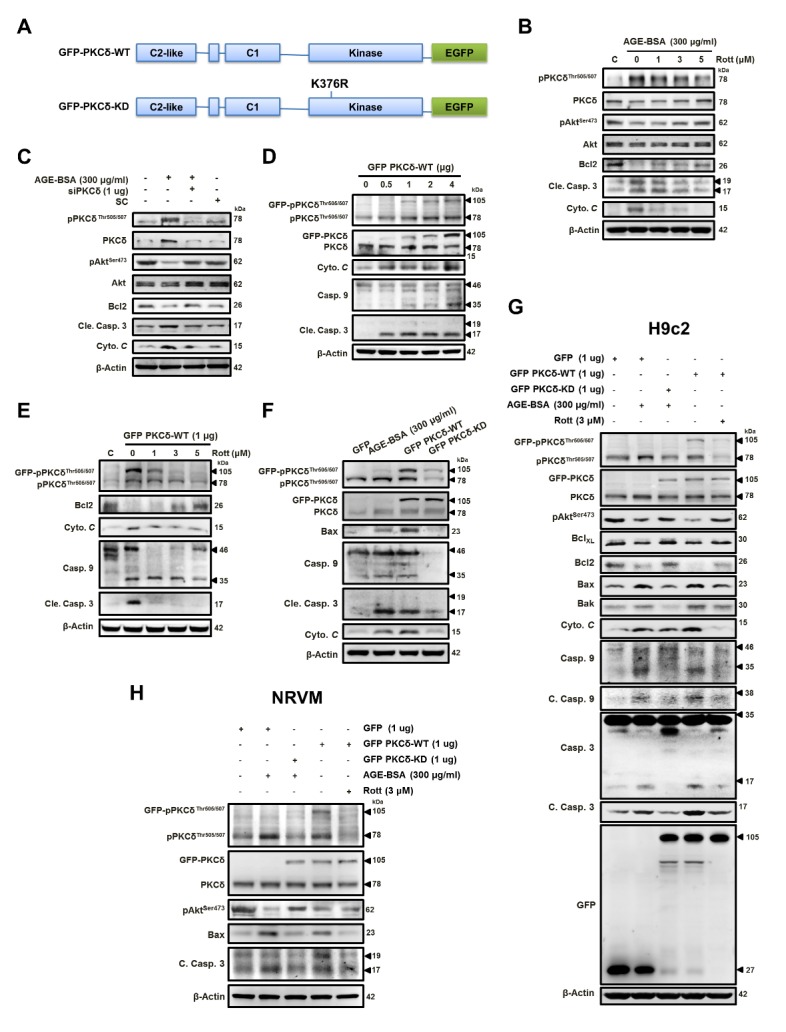
(A) The diagram depicts the domain organization of GFP-PKCδ. The GFP-PKCδ derivatives, including the wild-type (WT) and the kinase-deficient mutant (KD; K376R). Cells were treated with AGE-BSA (300 μg/ml) and (B) rottlerin (1-5 μM) or (C) PKCδ silencing. (D) Cells were transfected with GFP-fused PKCδ (GFP PKCδ-WT) at different doses as indicated and with (E) 1 μg rottlerin (1-5 μM). (F&G) H9c2 cells or (H) neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVM) were exposed to AGEs (300 μg/ml) with or without (GFP PKCδ-KD) transfection or transfected with GFP PKCδ-WT in the presence of rottlerin (3 μM) or not. These are cropped blots, full-length blots of PKCδ and pPKCδ are presented in Suppl. Figure S4. SC, scramble; WT, wild type; KD, kinase-deficient; All the proteins were analyzed by western blotting using β-actin as a loading control.
