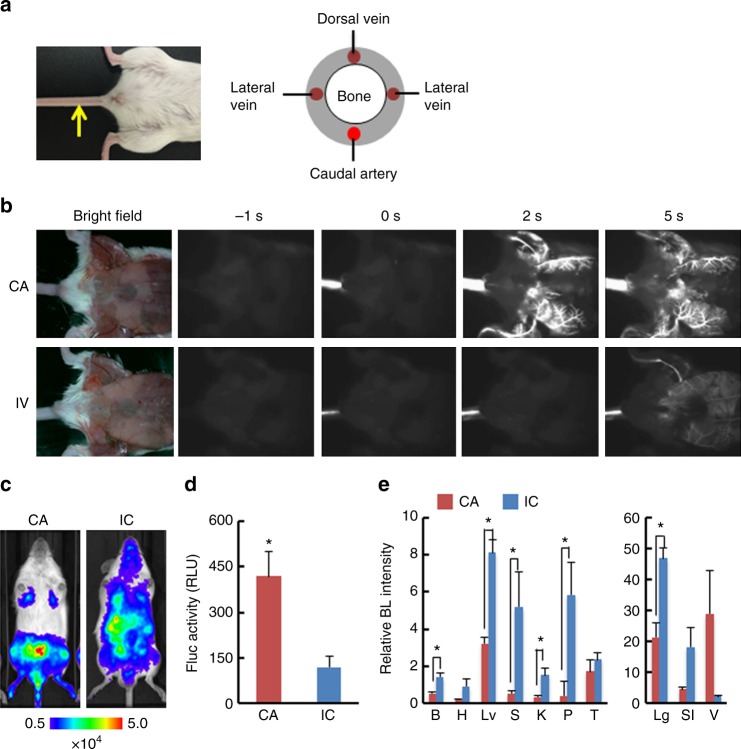
Fig. 1.
CA injection efficiently delivered cancer cells to bone marrow of a hind limb. a Location of caudal artery in a mouse (left) and a schematic of cross section of mouse tail (right). A yellow arrow indicates the caudal artery along the tail. b Comparison of fluorescence images after intra-caudal artery (CA) or tail vein (IV) injection of near-infrared II nanoparticles. c Representative BL images at 30 min after injecting LLC/luc cells through caudal artery (CA) or left ventricle (IC). d BL intensity of LLC/luc cells harvested from bone marrow of hind limbs at 30 min after CA or IC injection. n = 8, *P < 0.05 (two-side student’s t-test). Error bars indicate s.e.m. e Biodistribution of LLC/luc cells after CA or IC injection. Major organs were removed at 30 min after injecting LLC/luc cells and ex vivo BL imaging was performed. BL intensity of each organ was quantitatively analyzed and its relative BL intensity to the one in hind limb is shown. B brain, H heart, Lv liver, S spleen, K kidney, P pancreas, T testis, Lg lung, SI stomach and intestine, V vesicular gland. n = 3, *P < 0.05 (two-side student’s t-test)