Fig. 1.
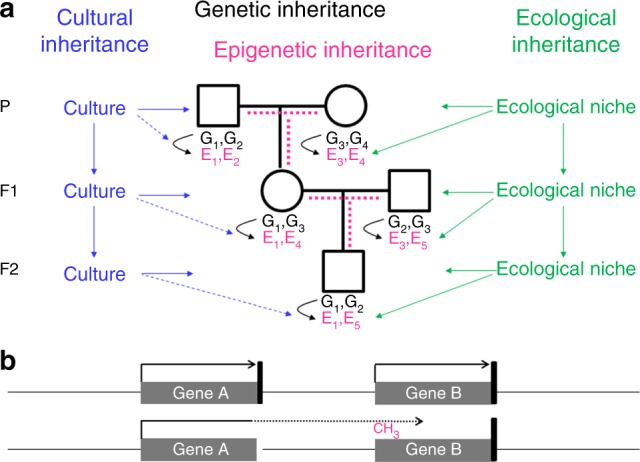
Transgenerational inheritance systems. a Offspring inherit from their parents genes (black), the environment (green) and culture (blue). Genes and the environment affect the epigenome (magenta) and the phenotype22. Culture also affects the phenotype, but at present there is no evidence for a direct effect of culture on the epigenome (broken blue lines). It is a matter of debate, how much epigenetic information is inherited through the germline (broken magenta lines). G genetic variant, E epigenetic variant. b An epimutation (promoter methylation and silencing of gene B in this example) often results from aberrant read-through transcription from a mutant neighboring gene, either in sense orientation as shown here or in antisense orientation. The presence of such a secondary epimutation in several generations of a family mimics transgenerational epigenetic inheritance, although it in fact represents genetic inheritance. Black arrow, transcription; black vertical bar, transcription termination signal; broken arrow, read-through transcription
