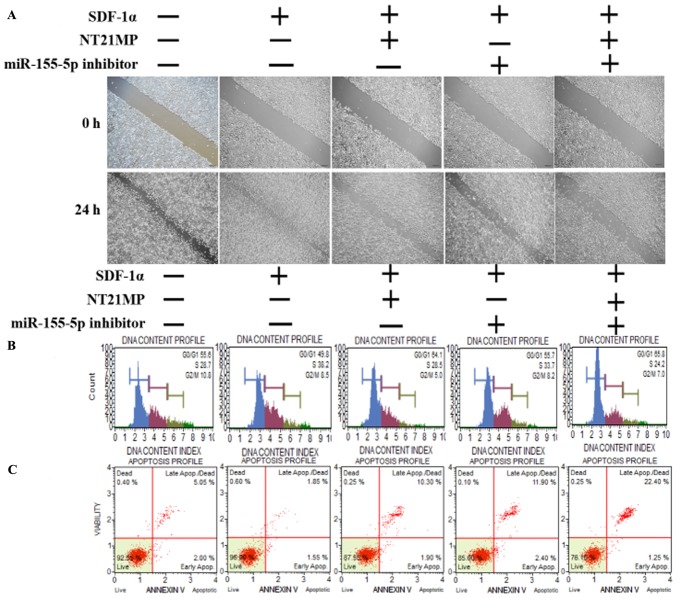
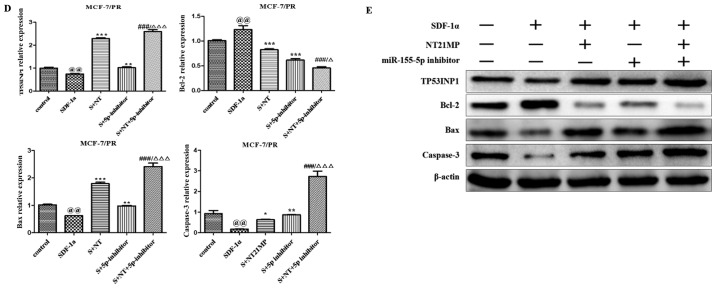
Figure 5.
Biological effects of NT21MP and miR-155-5p inhibitor on PR cells. (A) Effects of NT21MP and miR-155-5p inhibitor on cell migration and invasion were measured using the wound-healing assay. (B) Effects of NT21MP and miR-155-5p inhibitor on cell cycle were analyzed using PI staining and flow cytom-etry. (C) Effects of NT21MP and miR-155-5p inhibitor on cell apoptosis were evaluated using the Annexin V/PI staining and flow cytometry. (D) Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis was used to detect the effect of NT21MP and miR-155-5p inhibitor on the mRNA levels of target gene, cell cycle, and apoptosis-related factors. (E) Western blot analysis results of the protein levels of target genes, cell cycle, and apoptosis-related factors in PR cells were consistent with the mRNA results. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. @@P<0.01, compared with the control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, compared with SDF-1α treatment; ###P<0.001, compared with S + NT21MP treatment; ∆P<0.05 and ∆∆∆P<0.001, compared with S + 5p inhibitor treatment. NT21MP; 21-residue peptide derived from viral macrophage inflammatory protein II; miR, microRNA; S/SDF-1α, stromal cell-derived factor-1α; NT, NT21MP; PR, paclitaxel-resistant; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; TP53INP1, tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1; PI, propidium iodide.